Impact
On this page
Citations
Checking the impact of a single article
Checking the impact of articles within a topic
Altmetrics
Checking an author’s impact
Checking the impact of a journal
Relevant links
References
Impact is about the influence of researchers and their research on the scientific community. This is usually measured by the number of citations and the speed with which a publication is cited.
It is useful to know the authors and journals with the highest impact, because the more often an author has been cited the greater his authority in a scientific field and the more often an article has been cited, the better its impact and uptake in the scientific community.
Citations
Article databases such as Scopus, Web of Science Core Collection and Google Scholar provide a “times cited” number for each article. This number can help you assess the quality of an article. High citation numbers for an article may indicate an important source.
For an author, you can compose a citation overview or report. This provides a measure of the authority of an author. High citation numbers for an author over the years means more influence in the scientific field.
Checking the impact of a single article
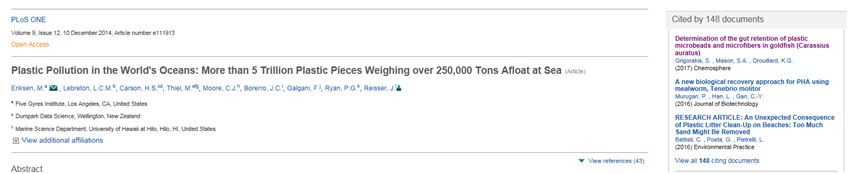
For example, you are interested Boyan Slat’s The Ocean Clean-upproject and you have found an article with the title “Plastic Pollution in the World’s Oceans”. From this point on you can determine the impact of the article by looking at the times cited number, in this case the article has been cited by 148 documents. Still, the amount of citations is just a number, so you have to see it in relation to other articles about the same subject.
Tip: You can study the “cited by” documents in order to broaden your knowledge about the subject and to shape your literature search.
Checking the impact of articles within a topic
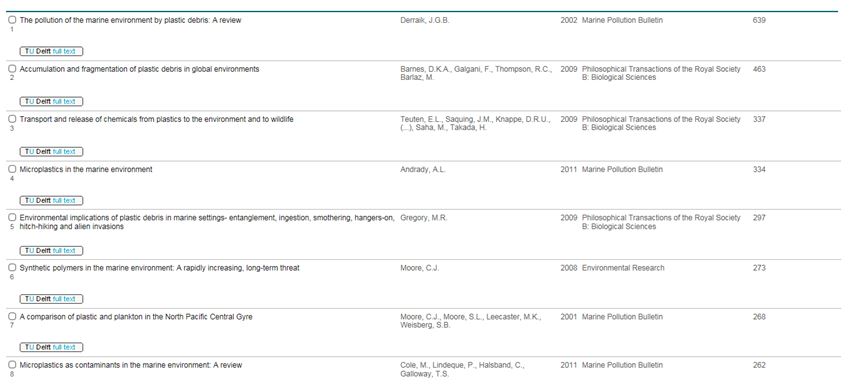
You search for relevant scientific articles about ocean clean-up. You can start by looking at the most cited articles. If you sort the documents on “cited by”, you will get a list of articles with the most cited articles on top.
High citation numbers for an article indicate that the article is an important source, but if an article is not cited it doesn’t mean that the content is not meaningful. Maybe the article has recently been published and has not been cited yet. So it is a good idea to check the relevance of the more recent publications as well as the most cited ones.
Tip: You can also check the authority of the authors of recently published articles by looking what they have already published about the subject.
Tip: It remains important to study the content of the selected articles. For information about studying literature, see: Reading for research.
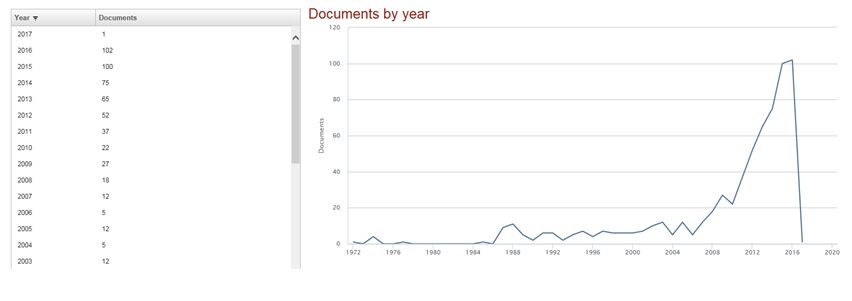
Tip: You can determine how current your subject is by using a tool to analyse your search results that is provided in Scopus, Web of Science and Google Scholar. In this way you can compose a graph with the articles per year.
Altmetrics
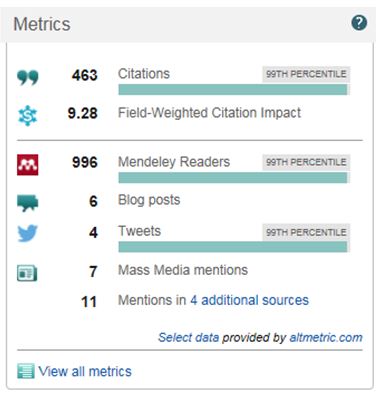
Altmetrics is another method used to determine the impact of a scientific publication. Nowadays the scientific communication has changed from paper to electronic. You can download scientific articles from for instance Google Scholar, scientists express themselves on social media and in the mass media there is attention for the results of scientific research.
Altmetrics measures the number of downloads of an article, the number of mentions in social media and the number of times scientific research is discussed in the mass media.
In addition it is possible to generate statistics from new tools like Mendeley. Altmetrics shows the number of times a publication is added to Mendeley libraries.
Checking an author’s impact
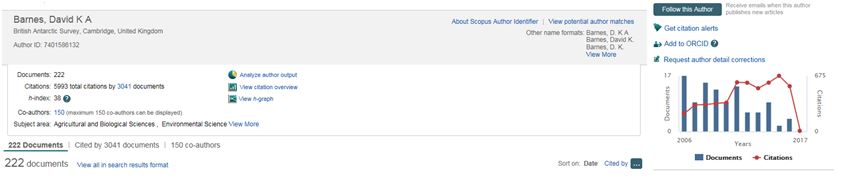
Many databases allow you to create an overview of an author’s publication and impact. For instance, this is the overview in Scopus of D.K.A. Barnes, who has published a great deal on sea pollution.
From this overview you can gain such information as the author’s number of publications and number of citations as well as his h-index. These will give you an indication of the influence of the author in his scientific field.
-
h-index
The h-index or Hirsch-index is a parameter that aims to quantify the scientific quality of an author by the number h of his papers that are cited at least h times. For example in the database Scopus, David K.A. Barnes has an h-index of 38. That means that the author’s first 38 papers, when ordered by number of citations, have all at least been cited 38 times.
In other databases, the same author will have different h-indexes, for instance in Google Scholar David K.A. Barnes has a h-index of 46 and in Web of Science a h-index of 36. The difference is caused by the content coverage of the databases: the calculation is based on a different set of publications.
While comparing h-indexes you need to compare authors in the same discipline and in the same database. Because of different citation patterns, an average medical researcher will generally have a much larger h-index than an excellent mathematician. In some disciplines in particular in humanities the h-index is less meaningful.
Checking the impact of a journal
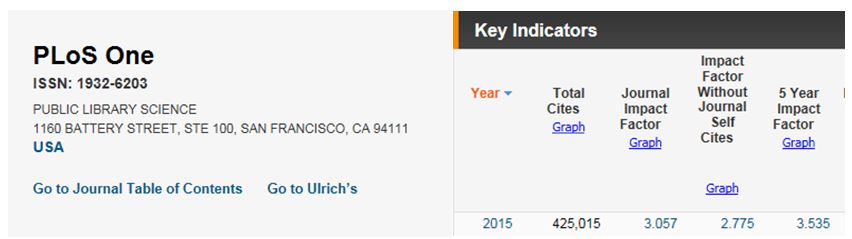
The impact of a journal is measured by the Journal Impact Factor. The impact factor of a journal is about citations to the articles in that journal. The greater the number of citations to articles in a specific journal, the higher the Journal Impact Factor of that journal. If a journal is cited on average once for each published article, its impact factor will be IF=1. Scientists want to publish in journals with high impact factors: it increases their authority in their scientific field and can also mean increased research funding. You can look up the impact factor of a journal in the Journal Citation Reports database (part of Web of Science).
Two other journal indicators are the Scimago Journal & Country Rank and SNIP indicator.
The SCImago Journal & Country Rank is a portal that includes not only journals but also country scientific indicators. These indicators are developed from the information contained in Scopus and can be used to assess and analyse scientific fields. Journals and country rankings can be compared or analysed separately.
The SNIP indicator (source normalized impact per paper) measures the average citation impact of the publications of a journal. Unlike the journal impact factor, SNIP corrects for differences in citation practices between scientific fields.
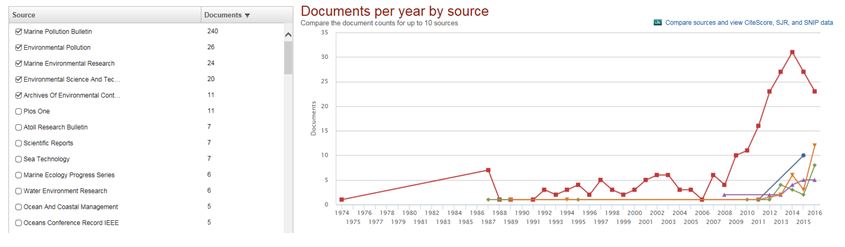
Tip: If you want to determine the most important journals in the scientific field, Scopus allows you to compose a graph of the articles per year by source.
Relevant links
Scopus (Database of peer-reviewed literature)
Web of Science (Subscription-based scientific citation indexing service)
Journal Citation Reports Database (A customized, citation-based research analytics tool)
SCImago Journal Rank (A measure of scientific influence of scholarly journals)
SNIP indicator (Measures the average citation impact of journal publications)
References
Restivo, D. (2009). Water drop impact on a water-surface [Image]. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Water_drop_impact_on_a_water-surface_-_(3).jpg
Ruiz-Grossman, S. (2016, August 6). 21-year-old’s miracle ocean-cleaning tech ready to get its feet wet. Huffington Post, edition US. http://www.huffingtonpost.com/entry/boyan-slat-ocean-clean-up-prototype-test-north-sea_us_5756fc1fe4b0b60682df0c90
Van der Salm, M. (2014, May 16). Altmetrics. http://leiden.scienceonline.com/blog/altmetrics