SESANS Spin-Echo Small-Angle Neutron Scattering
Spin-Echo Small-Angle Neutron Scattering (SESANS) is a powerful technique for studying structures in materials over several length scales, ranging from nanometres to microns. By using the spin properties of neutrons, SESANS encodes structural information into the neutron polarisation, allowing researchers to measure spatial correlations in complex samples like food materials, polymers, biological systems, and porous materials. Unlike most scattering methods, SESANS directly provides real-space data, simplifying interpretation. Its non-destructive nature and ability to probe deep within materials make SESANS a valuable tool for advancing knowledge in physics, chemistry, and materials science.
For a review of the technique applications: Spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering for multiscale structure analysis of food materials
W.G. Bouwman
Food Structure 30 100235 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foostr.2021.100235
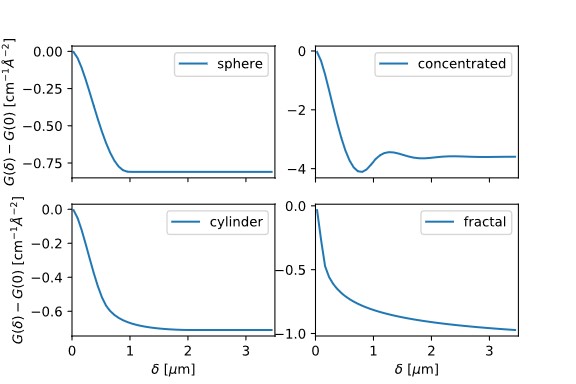
SESANS uses the principles of neutron spin echo to encode the scattering angle of the neutron irrespective of the collimation of the neutron beam, increasing the intensity of the neutron beam. The method is based on the Larmor precession of polarised neutrons in magnetic fields with inclined faces (the blue and red regions above indicate precession regions with opposite magnetic fields). This precession encodes the direction of the neutron trajectory. Without any scattering the precession yields a spin-echo with perfect polarisation. However, any scattering by the sample breaks the symmetry and decreases the polarisation of the beam. The measured polarisation is a Fourier transform of the scattering cross-section and thus closely related to the scattering length density correlation function, which facilitates data interpretation. The sensitivity can be tuned by varying the applied magnetic field B, the wavelength, the length of the set-up and the tilt angle of the interfaces. All these parameters can be combined into a single parameter, the spin-echo length, d, which is the length scale over which correlations in the sample are probed.
For the data-analysis: Analysis of SESANS data by numerical Hankel transform implementation in SasView
J.H. Bakker, A.L. Washington, S.R. Parnell, A.A. van Well, C.P. Pappas, W.G. Bouwman
J. of Neutron Research 22 57-70 (2020) https://doi.org/10.3233/JNR-200154
Analysis of spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering
R. Andersson, L.F. van Heijkamp, I.M. de Schepper, W.G. Bouwman
J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 868-885 (2008) http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0021889808026770
For the technique: Spin-echo small angle neutron scattering in Delft,
M.Th. Rekveldt, J. Plomp, W.G. Bouwman, W.H. Kraan, S.V. Grigoriev and M. Blaauw,
Review of scientific Instruments 76 033901 (2005) http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1858579
Applications
- Food materials, such as emulsions, protein gels and dairy products
- Polymers, such as composites and interpenetrating polymer networks
- Powders, such as spray dried granules and their agglomerates
- Colloids, for example to measure their interactions
- Nuclear graphite
Few examples
1. Food materials
In food many length scales can be of importance, especially in the micrometre range. Since food is soft, the surface can be rather different from the bulk structure. This makes that there are many applications with food. Food comes in the shape of colloids (casein micelles), gels (proteins) and fibres (meat analogues). The measurements give directly an impression of the measured structures.
Spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering for multiscale structure analysis of food materials
W.G. Bouwman
Food Structure 30 100235 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foostr.2021.100235
2. Polymer medical devices
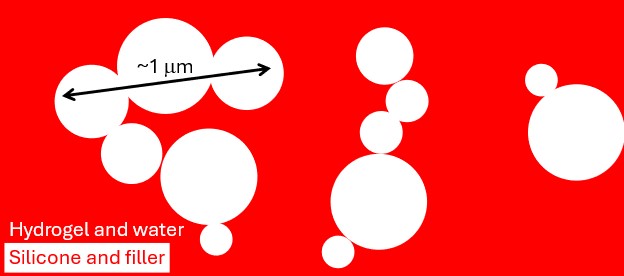
SESANS helped to improve the understanding of a new therapeutic drug delivery material in patches on the skin. The patches consist of silicone with embedded glycerol droplets that act as reservoirs for active substances. The neutrons allow you to see the inside of compound polymer materials. The neutron scattering showed that all the water in the system was located in the glycerol droplets, thereby discarding the hypothesis that the water flows in channels created by the glycerol droplets within the silicone matrix. This knowledge is essential when designing patches to deliver therapeutic drugs in a controlled and targeted way to the skin.
The microscopic distribution of hydrophilic polymers in interpenetrating polymer networks (IPNs) of medical grade silicone
G.N. Smith, E. Brok, M. Schmiele, K. Mortensen, W.G. Bouwman, C.P. Duif, T. Hassenkam, M. Alm, P. Thomsen, L. Arleth
Polymer 224 123671 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2021.123671
3. Tuneable interactions between colloidal particles
Spin-Echo Small-Angle Neutron Scattering (SESANS) provided unique insights into the phase behaviour of colloidal systems with short-range attractions and intermediate-range repulsions. The repulsion between the charged colloidal particle was tuned by adding salt. The long range attraction was tuned by adding polymers giving rise to depletion attraction. SESANS probes how the interplay between repulsion and attraction influence fluid-fluid separation, gelation, and structural inhomogeneities. This approach allows precise characterization of interaction potentials, enabling the rescaling of phase transitions with key parameters like the second virial coefficient and contact potential. The findings have broad implications for understanding and optimizing colloidal gels in industrial applications, from food to materials science, highlighting the interplay between attraction and repulsion in determining material properties.
The extended law of corresponding states when attractions meet repulsions
K. van Gruijthuijsen, M. Obiols-Rabasa, P. Schurtenberger, W.G. Bouwman, A. Stradner
Soft Matter 14 3704-3715 (2018) http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00160J
-
Specs of the instrument in the table
For a full description of our SESANS we recommend:
Spin-echo small angle neutron scattering in Delft,
M.Th. Rekveldt, J. Plomp, W.G. Bouwman, W.H. Kraan, S.V. Grigoriev and M. Blaauw,
Review of scientific Instruments 76 033901 (2005) http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1858579 -
The samples have to be non-magnetic, should transmit the neutrons, have a size comparable to the beam size and should have a scattering power between 0.1 and 1, optimally 0.3. The scattering power for a two phase system can be calculated as the product of the neutron wavelength squared, the sample thickness, the relevant length scale in the sample, and the scattering length density contrast squared: t = l2 t x (Dr)2. For liquid samples, typically Helma cells with a width of 18 mm are used with a thickness in the range between 1-10 mm. Banjo cells are a good alternative. Solid samples can be packed in aluminium foil or directly put in the beam.
More details on the scattering power calculation can be found in:
Analysis of spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering
R. Andersson, L.F. van Heijkamp, I.M. de Schepper, W.G. Bouwman
J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 868-885 (2008) http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0021889808026770 -
There are several automatic sample changers, with place for 5 – 15 samples. One of them is temperature controlled with a water bath in the range between -10-80 degrees Celsius. There is a rotating sample stage for 3 samples to prevent the samples from sedimentation or creaming.
Please check out the info at the page User Office for Proposal Application, Contact Information and FAQ/QA.
- Revealing microscale bulk structures in polymer–carbon nanocomposites using spin-echo SANS
L.V. Tiihonen, M.P. Weir, A.J. Parnell, S.C. Boothroyd, D.W. Johnson, R.M. Dalgliesh, M. Bleuel, C.P. Duif, W.G. Bouwman, R.L. Thompson, K.S. Coleman, N. Clarke, W.A. Hamilton, A.L. Washington, S.R. Parnell
Soft Matter 20, 8663- 8674 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM00578C
- Simulations of spin-echo SANS (SESANS) using McStas on monochromatic and time of flight instrument
S.R. Parnell, F. Li, W. Stevense, W.G. Bouwman
Journal of Neutron Research 26, 35-46 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.3233/JNR-240004
- Simulations and concepts for a 2-D spin-echo modulated SANS (SEMSANS) instrument
S.R. Parnell, S. van den Berg, G. Bolderink, W.G. Bouwman
Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2481, 012007 (2023)
https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2481/1/012007
- Time-of-flight spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering applied to biological cell nuclei
E.G. Iashina, W.G. Bouwman, C.P. Duif, R. Dalgliesh, E.Y. Varfolomeeva, R.A. Pantina, R.A. Kovalev, N.D. Federova, S.V. Grigoriev
J. Appl. Cryst. 56 1512-1521 (2023)
https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600576723007549
- Radial spin echo small-angle neutron scattering method: concept and performance
E. Kadletz, W.G. Bouwman, C. Pappas
J. Appl. Cryst. 55 1072-1084 (2022)
https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600576722007245
- Spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering for multiscale structure analysis of food materials
W.G. Bouwman
Food Structure 30 100235 (2021)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foostr.2021.100235
- The microscopic distribution of hydrophilic polymers in interpenetrating polymer networks (IPNs) of medical grade silicone
G.N. Smith, E. Brok, M. Schmiele, K. Mortensen, W.G. Bouwman, C.P. Duif, T. Hassenkam, M. Alm, P. Thomsen, L. Arleth
Polymer 224 123671 (2021)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2021.123671
- Structural characterization of spray-dried microgranules by spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering
Priyanka Biswas, Debasis Sen, W.G. Bouwman
Powder Technology 378 680-684 (2021)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.10.035
- Mesoporous silica formation mechanisms probed using combined Spin-Echo Modulated Small Angle Neutron Scattering (SEMSANS) and Small Angle Neutron Scattering (SANS)
J. Schmitt, J.J. Zeeuw, J. Plomp, W.G. Bouwman, A. Washington, R.M. Dalgliesh, C.P. Duif, M.A. Thijs, F. Li, R. Pynn, S.R. Parnell, K.J. Edler
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 12 28461-28473 (2020)
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c03287
- Small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) and spin-echo SANS measurements reveal the logarithmic fractal structure of the large-scale chromatin organization in HeLa nuclei
E.G. Iashina, M.V. Filatov, R.A. Pantina, E.Yu. Varfolomeeva, W.G. Bouwman, C.P. Duif, D. Honecker, V. Pipich, S.V. Grigoriev
J. of Appl. Cryst. 52 844-853 (2019)
https://doi.org/10.1107/S160057671900921X
- Fibre formation in calcium caseinate influenced by solvent isotope effect and drying method – A neutron spectroscopy study
B.Tian, V. Garcia Sakai, C.P. Pappas, A.J. van der Goot, W.G. Bouwman
Chemical Engineering Science 207 1270-1277 (2019)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2019.07.023
- Systematically quantifying oil–water microemulsion structures using (spin-echo) small angle neutron scattering
M. Mulder, X.X. Li, M.M. Nazim, R.M. Dalgliesh, B. Tian, M. Buijse, J. van Wunnik, W.G. Bouwman
Colloids and Surfaces A 575 166-175 (2019)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.04.045
- Evolution of dispersion in the melt compounding of a model polymer nanocomposite system: A multi-scale study
H. Gaspar, R. Santos, P. Teixeira, L. Hilliou, M.P. Weir, C.P. Duif, W.G. Bouwman, S.R. Parnell, S.M. King, J. A. Covas, G. Bernardo
Polymer testing 76 109-118 (2019)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2019.03.013
- Visualizing the heterogeneous breakdown of a fractal microstructure during compaction by neutron dark-field imaging
R. P. Harti, J. Valsecchi, P. Trtik, D. Mannes, C. Carminati, M. Strobl, J. Plomp, C. P. Duif, C. Grünzweig
Scientific Reports 8 17845 (2018)
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35845-y
- Air bubbles in fibrous caseinate gels investigated by neutron refraction, X-ray tomography and refractive microscope
B.Tian, Z. Wang, A.J. van der Goot, W.G. Bouwman
Food Hydrocolloids 83 287-295 (2018)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.05.006
- The extended law of corresponding states when attractions meet repulsions
K. van Gruijthuijsen, M. Obiols-Rabasa, P. Schurtenberger, W.G. Bouwman, A. Stradner
Soft Matter 14 3704-3715 (2018)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00160J
- Additive scaling law for structural organization of chromatin in chicken erythrocyte nuclei
E.G. Iashina, E.V. Velichko, M.V. Filatov, W.G. Bouwman, C.P. Duif, A. Brulet, S.V. Grigoriev
Physical Review E 96 012411 (2017)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.96.012411
- Spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering study of the structure organization of the chromatin in biological cells
E.G. Iashina, W.G. Bouwman, C.P. Duif, M.V. Filatov, S.V. Grigoriev
J. of Physics: Conf. Series 862 012010 (2017)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/862/1/012010
- Investigation of the closed porosity of functional ceramic materials by spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering
H. Gaspar, P. Teixeira, R. Santos, L. Fernandes, L. Hilliou, M. P. Weir, A. J. Parnell, K. J. Abrams, C. J. Hill, W. G. Bouwman, S. R. Parnell, S. M. King, N. Clarke, J. A. Covas, G. Bernardo
Macromolecules 50 3301-3312 (2017)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.6b02283
- Investigation of the closed porosity of functional ceramic materials by spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering
K. A. Pavlov, E. V. Velichko, V. N. Zabenkin, W. H. Kraan, C. P. Duif, W. G. Bouwman, Z. A. Mikhailovskaya, E. S. Buyanova, S. V. Grigoriev
J. of Surface Investigation: X-ray, Synchrotron and Neutron Techniques 11 92-98 (2017)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S1027451017010189
- High-strength bacterial cellulose–polyacrylamide hydrogels: Mesostructure anisotropy as studied by spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering and cryo-SEM
E.V. Velichko, A.L. Buyanov, N.N. Saprykinac, Yu.O. Chetverikov, C.P. Duif, W.G. Bouwman, R.Yu. Smyslov
European Polymer Journal 88 269-279 (2017)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2017.01.034
- Characterization of the Stratified Morphology of Nanoparticle Agglomerates
A. Fabre, T. Steur, W.G. Bouwman, M.T. Kreutzer, J.R. van Ommen
J. Phys. Chem. C 120 20446–20453 (2016)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b07437
- From nanopores to macropores: Fractal morphology of graphite
Z. Zhou , W.G. Bouwman, H. Schut, S. Desert, J. Jestin, S. Hartmann, C. Pappas
Carbon 96 541-547 (2016)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2015.09.069
- Microstructure and rheology of globular protein gels in the presence of gelatin
Carsten Ersch, Marcel Meinders, W.G. Bouwman, M. Nieuwland, E. van der Linden, P. Venema, A.H. Martin
Food Hydrocolloids 55 34-46 (2016)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.09.030
- Relating water holding of ovalbumin gels to aggregate structure
M. Nieuwland, W.G. Bouwman, L. Pouvreau, A.H. Martin, H.H.J. de Jongh
Food Hydrocolloids 52 87-94 (2016)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.06.018
- Characterizing length scales that determine the mechanical behavior of gels from crosslinked casein micelles
M. Nieuwland, W.G. Bouwman, M.L. Bennink, E. Silletti, H.H.J. de Jongh
Food Biophysics 10 416-427 (2015)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11483-015-9399-y
- On characterization of anisotropic plant protein structures
G.A. Krintiras, J. Göbel, W.G. Bouwman, A.J. van der Goot and G.D. Stefanidis
Food & Function 5 3233-3240 (2014)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C4FO00537F
- Multidimensional Nature of Fluidized Nanoparticle Agglomerates
L. de Martin, W.G. Bouwman and J.R. van Ommen
Langmuir 30 12696-12702 (2014)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/la502987e
- Direct comparison of SESANS and SAXS to measure colloidal interactions
K. van Gruijthuijsen, W.G. Bouwman, P. Schurtenberger and A. Stradner
EPL 106 28002 (2014)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/106/28002
- DCD USANS and SESANS: a comparison of two neutron scattering techniques applicable for the study of large-scale structures
C. Rehm, J. Barker, W.G. Bouwman, R. Pynn
J. of Appl. Cryst. 64 354-364 (2013)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0021889812050029
- Using a grating analyser for SEMSANS investigations in the very small scattering angle range
M. Strobl, F. Wieder, C.P. Duif, A. Hilger, N. Kardjilov, I. Manke, W.G. Bouwman
Physica B 407 4132-4135 (2012)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2012.06.036
- Combined SANS–SESANS, from 1 nm to 0.1 mm in one instrument
W.G. Bouwman, C.P. Duif, J. Plomp, A. Wiedenmann, R. Gähler
Physica B 406, 2357-2360 (2011)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2010.11.069
- Milk Gelation Studied with Small Angle Neutron Scattering Techniques and Monte Carlo Simulations
L.F. van Heijkamp, I.M. de Schepper, M. Strobl, R.H. Tromp, J.R. Heringa, W.G. Bouwman
J. Phys. Chem. A 114 2412-2426 (2010)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp9067735
- Spatial modulation of a neutron beam by Larmor precession
W.G. Bouwman, C.P. Duif, R. Gähler
Physica B 404 2585-2589 (2009)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2009.06.052
- Structure, anisotropy and fractals in compressed cohesive powders
R. Andersson, W.G. Bouwman, J. Plomp, F.M. Mulder, H.G. Schimmel, I.M. De Schepper
Powder Technology 189 6–13 (2009)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2008.05.010
- Structure in cohesive powders studied with spin-echo small angle neutron scattering
R. Andersson, W.G. Bouwman, S. Luding, I.M. de Schepper
Granular Matter 10 407-414 (2008)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10035-008-0109-z
- Analysis of spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering
R. Andersson, L.F. van Heijkamp, I.M. de Schepper, W.G. Bouwman
J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 868-885 (2008)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0021889808026770
- Stress, strain, and bulk microstructure in a cohesive powder
R. Andersson, W.G. Bouwman, S. Luding, I.M. de Schepper
Physical Review E 77 051303 (2008)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.77.051303
- Real-space neutron scattering methods
W.G. Bouwman, J. Plomp, V.O. de Haan, W.H. Kraan, A.A. van Well, K. Habicht, T. Keller, M.T. Rekveldt
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 586 9–14 (2008)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2007.11.045
- Polarization optimization of spin-echo small angle scattering instruments
M.Th.Rekveldt, C.P. Duif, W.H. Kraan, J. Plomp and W.G. Bouwman
Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79, 015113 (2008)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2832350
- Analysis of artificial silicon microstructures by ultra-small-angle and spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering
M. Trinker, E. Jericha, W.G. Bouwman, R. Loidl, H. Rauch
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 579 1081–1089 (2007)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2007.06.008
- Probing the droplet cluster structure in acidified temperature cycled o/w emulsion gels by means of SESANS
A. Bot, F.P. Duval, C.P. Duif and W.G. Bouwman
International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 42, 746–752 (2007)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2007.01539.x
- Neutron refraction by cylindrical metal wires
J. Plomp, J.G. Barker, V.O. de Haan, W.G. Bouwman, A.A. van Well
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 574 324–329 (2007)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2007.02.068
- Effect of processing on droplet cluster structure in emulsion gels
A. Bot, F.P. Duval, and, W.G. Bouwman
Food Hydrocolloids 21, 844–854 (2007)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2006.09.012
- Phase-object approximation in small-angle neutron scattering experiments on silicon gratings
V.O. de Haan, J. Plomp, W.G. Bouwman, M. Trinker, M.Th.Rekveldt, C.P. Duif, E. Jericha, H. Rauch and A.A. van Well
J. Appl. Cryst.. 40, 151–157 (2007)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0021889806047558
- A novel application of neutron scattering on dairy products
R.H. Tromp and, W.G. Bouwman
Food Hydrocolloids 21, 154-158 (2007)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2006.02.008
- Light scattering measurements on microemulsions: Estimation of droplet sizes
C. Goddeeris, F. Cuppo, H. Reynaers, W.G. Bouwman and G. van den Mooter
Int. J. of Pharmaceutics 312, 187-195 (2006)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.01.037
- Spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering for magnetic samples
S.V. Grigoriev, W.H. Kraan, M.Th. Rekveldt, T. Kruglov and W.G. Bouwman
J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 252-258 (2006)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S002188980600481X
- Spin-echo small angle neutron scattering in Delft
M.Th. Rekveldt, J. Plomp, W.G. Bouwman, W.H. Kraan, S.V. Grigoriev and M. Blaauw
Review of scientific Instruments 76 033901 (2005)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1858579
- Structure of hard-sphere colloid observed in real space by spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering
T. Kruglov, W.G. Bouwman, J. Plomp, M.Th. Rekveldt, G.J. Vroege, A.V. Petukhov and D.M.E. Thies-Weesie
Physica B 357 452-455 (2005)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2004.12.032
- Application of spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering to study the structure of charged colloids
T.V. Krouglov, W.G. Bouwman, I.M. de Schepper and M.Th. Rekveldt
Physica B 356 218-222 (2005)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2004.10.080
- SESANS with a monochromatic beam or with time-of-flight applied on colloidal systems
W.G. Bouwman, W. Stam, T.V. Krouglov, J. Plomp, S.V. Grigoriev, W.H. Kraan and M.Th. Rekveldt
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A529 16-21 (2004)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2004.04.150
- SESANS studies of colloid phase transitions, dairy products and polymer fibres
W.G. Bouwman, T.V. Krouglov, J. Plomp, S.V. Grigoriev, W.H. Kraan and M.Th. Rekveldt
Physica B 350 140-146 (2004)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2004.04.013
- Neutron refraction and transmission studied by SESANS
M.Th. Rekveldt, W.G. Bouwman, W.H. Kraan and J. Plomp
Physica B 350 E791-E794 (2004)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2004.03.206
- Structural transitions of hard-sphere colloids studied by spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering
T.Krouglov, W.G. Bouwman, J. Plomp, M.Th. Rekveldt, G.J. Vroege, A.V. Petukhov and D.M.E. Thies-Weesie
J. Appl. Cryst. 36, 1417-1423 (2003)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0021889803021216
- Spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering to study particle aggregates
T.Krouglov,W.H. Kraan, J. Plomp, M.Th. Rekveldt and W.G. Bouwman
J. of Appl. Cryst. 36 816-819 (2003)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0021889803003984
Contact information