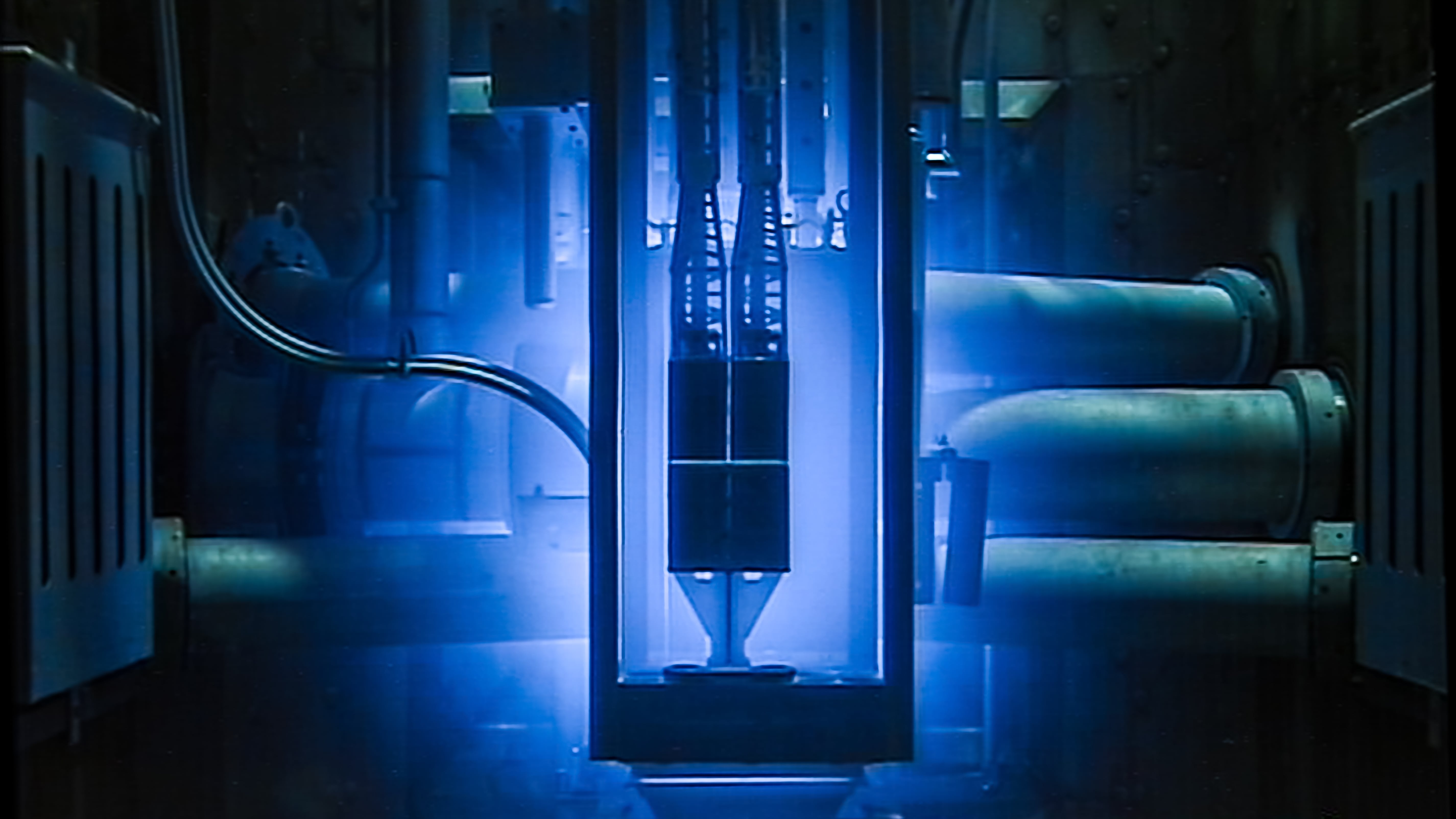
TU Delft launches future proof research reactor with cold neutron source
More advanced and faster research is possible with the commissioning of the cold neutron source and the improved instruments of TU Delft Reactor Institute (RID) as of 27 June 2024. The first results of research are expected in October 2024, around the official reopening of the reactor.
In recent years, the TU Delft team together with more than 10 national and international partners and suppliers have realised a technical masterpiece. So, the reactor is back in business and the blue light shines again. This masterpiece included installing a "neutron cooler" next to the reactor core, building all associated facilities and upgrading the measuring instruments. With these adjustments TU Delft Reactor Institute is one of the six research reactors in Europe where research can be done with a cold neutron source.
Research on materials
TU Delft Reactor Institute is investing constantly in improving measurement methods and research techniques to enable scientists to perform groundbreaking non-destructive research on materials with the research reactor. These efforts have now entered a new phase thanks to the finalization of the OYSTER programme: Optimized Yield – for Science, Technology and Education – of Radiation.
The cold neutron source plays a key role within Oyster. Cooled neutrons have more interaction with a research object than non-cooled neutrons. The quality and speed of measurements with cold neutrons can therefore be improved by a factor of a hundred. Wim Koppers, director of the Institute: “I am proud of the team’s achievements and look forward to receiving researchers and scientists from all over the world to use our research reactor!”
Funding
The programme has been financed with NWO funding.
Neutrons for research and education
The TU Delft Reactor Institute is the largest provider of research and education using radiation and nuclear techniques for materials for energy and health in the Netherlands. The demand in our society for these applications is only increasing, given the developments in the areas of health, energy and climate. This means that permanent and structural investments are needed in both our researchers and the TU Delft infrastructure.
Who can use the neutrons?
The research reactor is accessible to all researchers, from both the Netherlands, Europe as well as worldwide. Whether it is research by a public university or a private R&D department, researchers can use the equipment to dive deep into the structure of materials. Examples include research into lithium batteries and solar cells, improving the structure of meat replacements, the development of a sensor for hydrogen as well as new production methods for medical isotopes to diagnose and treat cancer.
Want to know more?
Would you like more information about the possibilities TU Delft Reactor Institute has to offer for research into products and materials? Then take a look at our research instruments.
TU Delft Reactor Institute Femke Werkman: f.m.werkman@tudelft.nl
Press officer TU Delft Dave Boomkens: d.j.boomkens@tudelft.nl
Background information on neutrons for research:
What can you see with neutrons?
Neutrons enable researchers to characterize materials in detail and reveal the atomic and magnetic structures as well as dynamics without damaging the materials. This opens up opportunities to researchers working in condensed matter physics and chemistry, nanotechnology, polymer science, life science, sustainable energy research, sensors and smart materials, biotechnology, engineering and archaeology. The output of the research results contributes to solving societal challenges in many sectors such as energy, health and food.
Why cold neutrons?
Neutrons help to give insight into the structure and dynamics of materials such as colloids, hydrogen, lithium, metals or surfactants. Cooling the neutrons provides the researchers with more possibilities: they have more neutrons available, they can “guide” the particles better, they need less “beam” time for measurements and they can measure at wavelengths that were previously not possible. All-in-all, they get more detail out of the measurements. And what is also kept the same: the material is not damaged.
Improvement instruments and infrastructure
During the past years a number of improvements have been made: a cold neutron source has been installed, accompanied by the improvement of existing instruments and development of new instruments. This unique project has been done with a dedicated group of employees and a number of subcontractors amongst others: KHC/KAERI, Korea who were responsible for the design and fabrication of the actual cold neutron source. Billfinger- Germany took care of the installation of the cold neutron source. Strukton, Netherlands were in charge of design and construction of the necessary utility systems. Other contractors who were part of the project: Strukton Worksphere, Stirling Cryogenics Netherlands, Demaco Netherlands, Yokogawa, Kreber, Stork, RHDHV, Arcadis, Lloyds/ LRQA, NRG and Combigas.
TU Delft Reactor Institute
For over 60 years, the TU Delft Reactor Institute and the scientific department Radiation Science & Technology have formed the Dutch centre of excellence on nuclear technologies and the use of ionizing radiation for research and education.
With our knowledge and expertise, we make an important contribution to scientific research using neutrons, positrons, electrons, protons, gamma radiation and radioisotopes. Much of the research focuses on the development of new materials for sustainable energy such as solar cells, batteries and economical cooling/heating. We also work on medical applications, such as the production of medical isotopes for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. We also conduct research into clean and safe nuclear energy.
Our teaching activities include the training of bachelor and master students and PhD students. We also provide a wide range of courses in the fields of radiation hygiene and nuclear measurement techniques. We are the largest training provider in the Netherlands in the field of radiation hygiene, the discipline that ensures that people can work safely with radiation
Expertise/infrastructure and education for third parties
We are happy to use our expertise and the unique Delft nuclear research facilities and instruments to help scientists, companies and organisations with research and development. We are part of an international network of top institutes that we can turn to for additional measurements.
Development of products and materials
We are of great importance to a large group of (multinational) companies in the development of new products and services. In healthcare, we cooperate with academic hospitals and HollandPTC for new personalised treatment therapies to fight cancer. For the energy sector, we are developing better methods for storing energy with hydrogen and batteries and for efficient cooling and heating with new magneto-calorific materials. TU Delft Reactor Institute acts both as knowledge carrier and developer of fundamental knowledge.