Nature publication on loops, flags and tension in DNA
Two protein complexes carry the major responsibility for the spatial organisation of chromosomes in our cell nuclei. DNA tension plays a surprising role in this. Together with Austrian colleagues, nanoscientist Cees Dekker and his PhD candidate Roman Barth of the Kavli Institute of Nanoscience at TU Delft now publish how they have visualised this in detail in Nature on April 19.
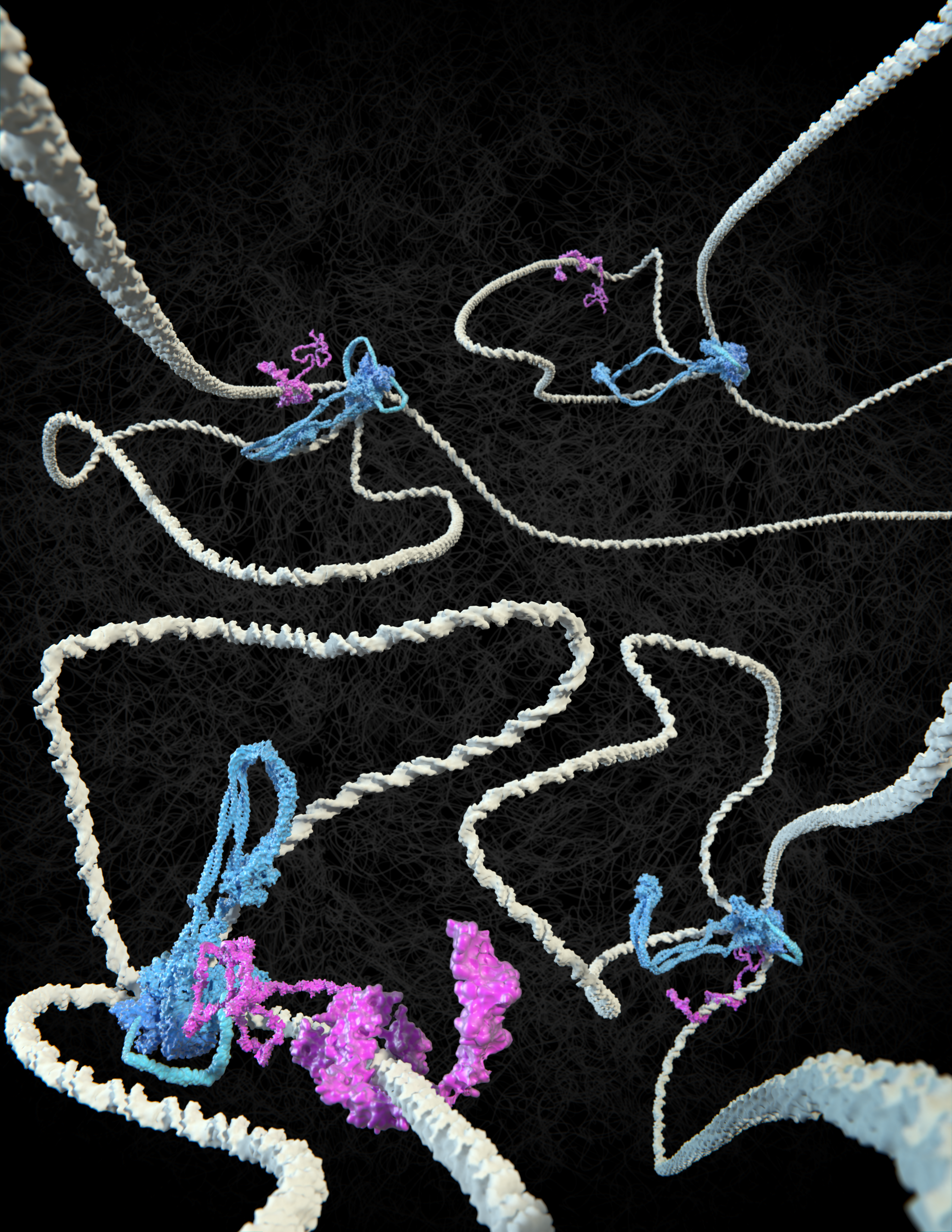
#1 Cohesin loops DNA
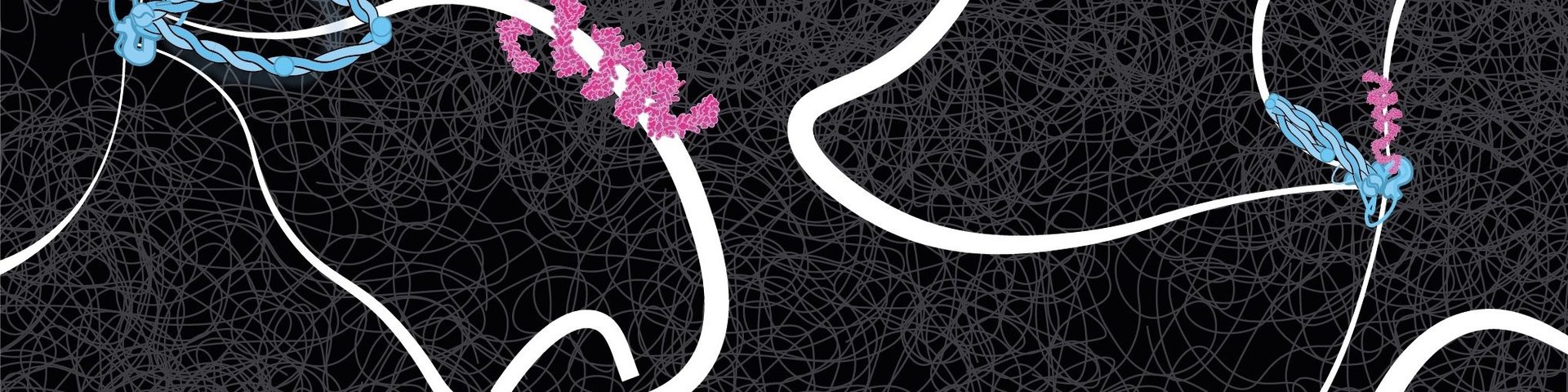
It has been known for more than a century that the long DNA strands in cell nuclei are neatly folded into the characteristic shape of chromosomes, resembling bottlebrushes , in preparation for cell division. And also between divisions, chromosomes are organised into loops that are important for regulating the processing genetic information. In 2018, Dekker and his group were the first to visualise how SMC protein complexes such as condensin and cohesin extrude loops in DNA.
#2 CTCF flags have a direction and determine where a loop begins and ends…
The DNA-binding protein CTCF was found to play a key role in the positioning of loops along the genome. Dekker: “If you think of DNA as a rope, onto which CTCF flags are pinned at two points, cohesin makes the loops from one flag to the other, but only if the CTCF is oriented correctly. Only one side of the CTCF protein is able to interact with cohesin. Then again, it doesn’t always do this, because we thought CTCF would also fail frequently. But now we have measured it. The interaction between the two proteins turns out to be much more subtle than we predicted.”
That CTCF and cohesin work together to establish loop boundaries has become basic knowledge in the field, says PhD candidate Roman Barth: “In every conference presentation I attended in the past year, the basic premise was that the cohesin complex extrudes loops between correctly oriented CTCF molecules. But nobody had ever seen in detail how that happens. We have now been able to visualise the essence of this.”
#3: … And DNA tension plays a surprising role in this
Colleagues in Jan-Michael Peters’ group at the Institute of Molecular Pathology in Vienna succeeded in making the proteins available in pure form. The two ends of a DNA molecule were attached to a surface; the DNA and proteins were stained with a fluorescent dye. The researchers then made an unusual discovery, Dekker explains. “In the data, Roman discovered that it made a difference whether the DNA strand was very loose or under tension. Without tension, cohesin often ignored the CTCF flag, even if correctly oriented, but when the DNA was under more tension, the CTCF acted as a perfect barrier. So, under the influence of DNA tension, CTCF becomes like a smart traffic light, allowing cohesin to pass or not, depending on the local traffic situation.”
When cohesin collides with a CTCF protein, it can stop or continue. The researchers saw that it can also turn around, or even dissolve altogether. How and why this happens are the next questions Dekker hopes to answer.
More information on the publication:
CTCF is a DNA-tension-dependent barrier to cohesin-mediated loop extrusion
Iain F. Davidson, Roman Barth, Maciej Zaczek, Jaco van der Torre, Wen Tang, Kota Nagasaka, Richard Janissen, Jacob Kerssemakers, Gordana Wutz, Cees Dekker & Jan-Michael Peters
Nature 19 April 2023
Contact details
Professor Cees Dekker, Distinguished University Professor of Molecular Biophysics and Head of the Cees Dekker Lab.
Email c.dekker@tudelft.nl
Tel. +31 15 278 6094
Health & Care TU Delft
Healthcare is under pressure. Medical professionals want to offer their patients the best and the right care, but face staff shortages, rising healthcare costs and a substantial sustainability problem, among others. In collaboration with medical professionals, TU Delft is working on the long-term sustainability of healthcare. Through research and innovation, TU Delft aims to improve patient care and the work of healthcare professionals, and to future-proof and crisis-proof the complex and often inefficient healthcare system.
With over 30% health-related research, a top clinical hospital on our doorstep, and two major academic hospitals in the region, TU Delft makes a global impact.
Whether developing medical instruments, monitoring, remote care, imaging & sensing, rapid diagnostics or clinical research. Delft engineers are the ideal partner; from the start they work together as a team, involve patients in their research and test as much as possible in healthcare practice. As a result, new technologies are more applicable in practice and find their way more quickly to the OR, the consulting room and the patient's bedside.
TU Delft. Impact for a better society.