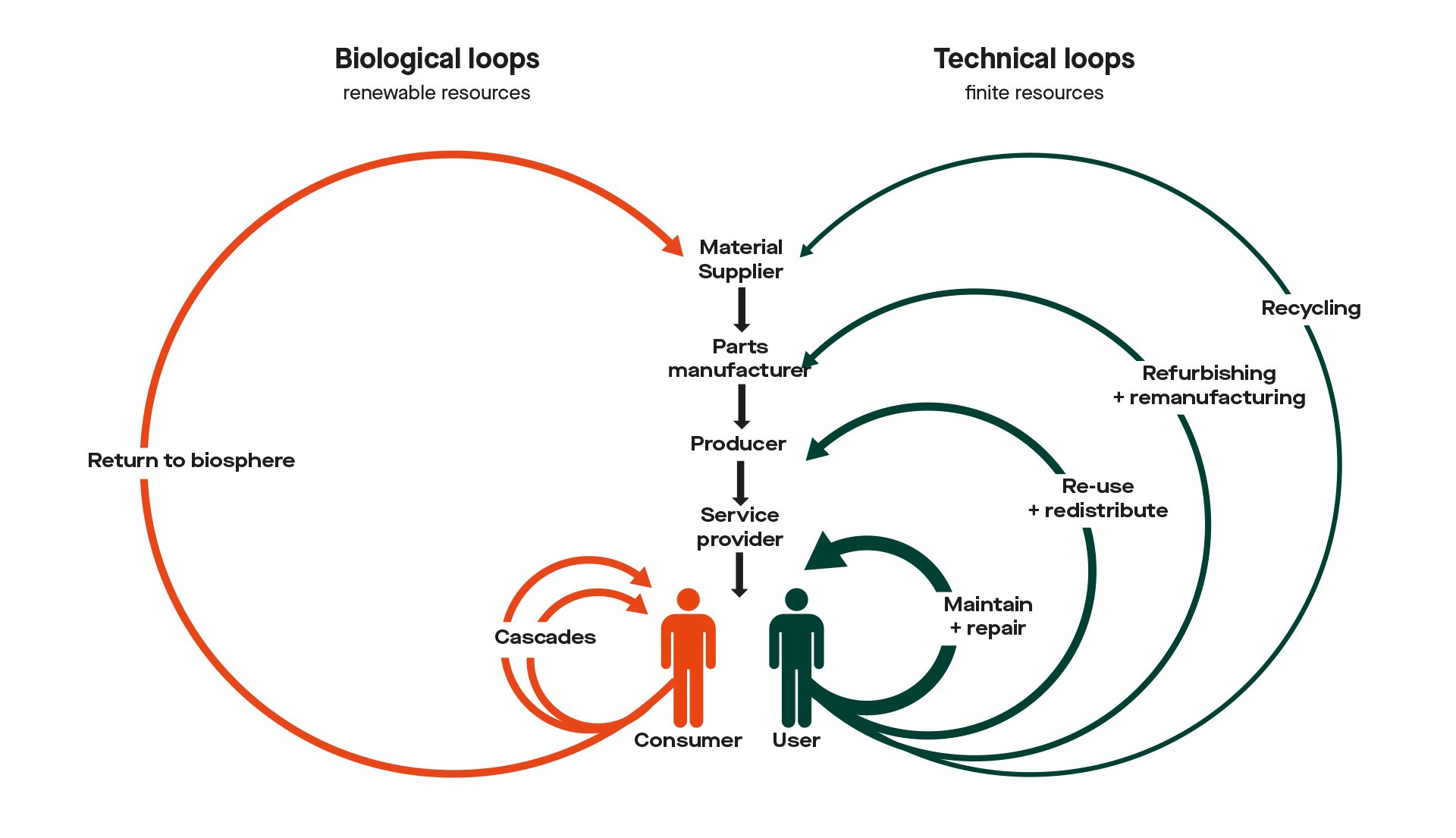
The 'butterfly model' of the circular economy, with adaptations adopted from The Ellen MacArthur Foundation (2017).
From linear to loops
The linear economic model of take-make-use-dispose consumes additional resources and produces increased waste and emissions. The construction industry is a major transgressor here. In the circular economy, raw materials are reused at the highest level of quality possible. The goal is to reduce consumption of resources and avoid producing waste and emissions. This is achieved by using 'loops' within which a product is directly reused, refurbished or recycled.
Making existing homes circular
A large part of the built environment consists of housing. When existing houses are made circular, demolition is no longer required. This prevents waste as well as the need to use new resources to construct replacement buildings. Existing homes are made circular by gradually replacing building components – such as roofs, facades and kitchens – with circular components during maintenance or renovation.
The circular kitchen as an accelerator
Kitchens are replaced frequently in comparison to other components like roofs and facades because a kitchen’s functional lifespan (how long it meets the user's (aesthetic) requirements) and technical lifespan (how long it functions as intended) are generally much shorter. As kitchens are replaced relatively often, the circular kitchen is an ideal pioneer in the transition to a circular built environment.
Environmental impact
The environmental impact of a kitchen can be reduced by using less material during a kitchen's lifespan, by using them for longer periods and by ultimately recycling the materials.
Functioning
The parties involved in this project have together determined the minimum requirements that a kitchen must meet along with aspects which have added value. We test these ideas by installing prototypes in the houses owned by our partners and asking the residents to share their experiences.
Affordable
A sustainable product only has a genuine impact when there is large-scale adoption. Affordability helps make the circular kitchen accessible to the widest possible user base. In addition, the purchase price is a long-term investment because users are able to enjoy a circular kitchen for longer than they would a traditional version.