Max-SCORE: Maximizing SCrap in COnverter REfinging
Shifting the limits of scrap usage in steelmaking converters to minimize CO2 emissions
Neodymium-Iron-Boron (NdFeB) based permanent magnets are indispensable for today’s technology-driven society, and this dependence is likely to increase. They are used in a variety of applications such as robotic systems and home appliances; they are also essential for clean energy applications such as hybrid/electric vehicles and wind turbines.
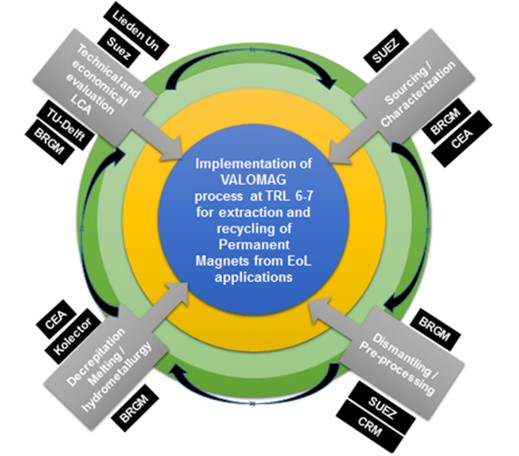
VALOMAG consortium, coordinated by SUEZ and in partnership with TU Delft, Leiden University and other 4 EU industry and research institutes (Kolector, BRGM, CEA, and CRM) receives an EIT RM funded upscaling project in the 2019 KAVA call. The VALOMAG project proposes to supply a technical solution for permanent magnet disassembly of EOL applications like hard disc drives, electric vehicles and wind turbines and to assess two short loop recycling technologies (HD/HDDR and strip-casting) for high and medium quality EOL magnets with a third alternative route using hydrometallurgical processes for low quality magnets waste. The project combines different key players who bring together their expertise to develop a new value proposal which answers the increasing demand of the rapidly growing permanent magnets market.
VALOMAG project runs for 3 years (2020-2022). The project has a total budget of 2.5 M€, of which EIT RM will provide 2 M€ for all 7 project partners. TU Delft team (MPRR group) will receive 400 k€ for a period of 3 years, and will focus on process integration and value chain analysis, and at the same time will be responsible for Work packages of “Dissemination, Communications and Education” (WP6 & WP7).
More information of the project could be found at the VALOMAG project webpage: https://www.valomag.tudelft.nl