Appendices
Appendix A. Overviews
-
Click on the conditions to go to the explanation in the framework. The conditions are listen in the order in which they appear in the text.
Condition 1: TU Delft, the faculties, the programme directors, and the examiners consciously consider the assessment values and quality requirements for assessments in their decisions about assessment. Condition 2: TU Delft, the faculties and the programme directors ensure that all assessment building blocks are of good quality and consistent with each other. The quality of these building blocks is systematically assessed and improved at least once every six years (see quality assurance plan). Condition 3: TU Delft ensures that the central quality assurance plan and the TU Delft assessment framework are aligned. Condition 4: The faculties ensure that their quality assurance handbook and their assessment policy comply with each other (including the evaluation frequency), and that both documents comply with the TU Delft framework. Condition 5: The TU Delft ensures that the available assessment tools support the goals of digital assessment tools (see ‘Goal of digital assessment tools’ in 1.4). Condition 6: The TU Delft and the faculties ensure that the owners of the assessment documents mentioned in Appendix B keep these up-to-date and congruent (consistent with each other). Condition 7: The TU Delft and the faculties ensure that students, teaching staff and other stakeholders are informed on their rights and obligations and in changes thereof (see Table 5). Condition 8: The TU Delft and the faculties ensure that the assessments comply with the legal framework as described in Appendix B of this framework. Condition 9: The TU Delft ensures that the assessment framework meets and operationalises the requirements of the institutional audit. Condition 10: The faculties ensure in the faculty’s assessment policy that their programmes live up to standard 3 (assessment) and 4 (achievement of the programme's final attainment levels) of the assessment framework of the NVAO. Condition 11: TU Delft and the faculties ensure that the assessments follow the TU Delft assessment agreements, listed in chapter 3. Condition 12: The directors of education ensure that their faculty has an up-to-date assessment policy which is in line with the TU Delft assessment framework and that operationalises the topics listed in 4.1. Condition 13: The programme directors ensure that their programme has an up-to-date programme assessment plan that is in line with their faculties’ assessment policy, and that operationalises the topics listed in 4.2. Condition 14: The course examiners ensure that their course has an up-to-date course assessment plan that shows how the learning objectives are assessed formatively and summatively. The course assessment plans are in line with the applicable programme assessment plan and faculty assessment policy, and operationalise at least the topics listed in 4.3. Condition 15: The programme directors ensure that their graduation projects have an up-to-date graduation manual that is in line with the programme assessment plan and with regulations. The manual contains the topics listed in 4.4. Condition 16: TU Delft, the faculties and the boards of examiners ensure that the tasks and responsibilities of the different stakeholders with respect to assessment are clear. Condition 17: The boards of examiners secure that graduates meet the final attainment levels of the programme by executing their legal tasks, listed in 5.9. Condition 18: TU Delft and the faculties support the programmes, and the courses in the process and execution of assessments. Condition 19: TU Delft ensures that educational and assessment quality are explicitly mentioned in both the HR recruitment and professional development policy. Condition 20: TU Delft ensures that the assessment training offer of Teaching and Learning Services (LS) is integrated in the HR training offer. Condition 21: TU Delft offers training opportunities on assessment to staff. Condition 22: The boards of examiners ensure that all appointed examiners have a UTQ qualification and that other assessors work under the responsibility of an examiner. Condition 23: The boards of examiners determine prerequisites on who may carry out key assessment tasks. Condition 24: The boards of examiners have regulations on the composition of the graduation committee to ensure assessment quality of graduation projects. Condition 25: TU Delft ensures that the HR system keeps track of at least the relevant assessment qualification of staff, listed in 6.5. Condition 26: TU Delft and the faculties ensure that new employees receive the required information and training in order to carry out their assessment tasks. Condition 27: TU Delft and the faculties make relevant assessment information available for stakeholders. Condition 28: Assessment experts within TLS and the faculties offer support and advice on assessment. -
National regulations & guidelines
1 Wet op het hoger onderwijs en wetenschappelijk onderzoek (2021). https://wetten.overheid.nl/BWBR0005682/.
27 Selectielijst Universiteiten en Universitair Medische Centra 2020 (2020). Werkgroep Acquisitie Selectie en Waardering van het Universitaire Platform Informatiedienstverlening en Recordmanagement. https://www.nationaalarchief.nl/archiveren/kennisbank/selectielijst-universiteiten-en-universitair-medische-centra-2020.
31 Wet gelijke behandeling op grond van handicap of chronische ziekte (2020). https://wetten.overheid.nl/BWBR0014915/2020-01-01.
51 4TU UTQ regulations (2018). 4TU Education Management Committee. https://www.utwente.nl/en/ces/celt/utq/4tu-utq-regulation-def-uk-08-03-17.pdf.
TU Delft regulations
2 Model Teaching and Examination Regulations TU Delft (TER) (2023). Executive Board TU Delft. Model Onderwijs- en Examenregeling (OER) TU Delft https://filelist.tudelft.nl/TUDelft/Over_TU_Delft/Organisatie/regelingen/Studenten%20en%20onderwijs/2021/RG%20BoE%20model%20ENG%202023-2024.pdf.
18 Rules of Procedures for Examinations (2020). Joint chairs of the Board of Examiners TU Delft. Reglement van Orde bij tentamens. https://www.tudelft.nl/en/about-tu-delft/organisation/regulations/students-and-education.
19 Online Proctored Examination Regulation (2020). Executive Board TU Delft. Regeling online proctored tentamen TU Delft. https://www.tudelft.nl/en/student/my-study-me/education/courses-and-examinations/examinations/online-proctored-examination-regulation
22 Joint model BSc / MSc Rules and Guidelines of the Board of Examiners 2023/2024 (2023). Executive Board TU Delft. Model Regels en Richtlijnen van de Examencommissie. https://filelist.tudelft.nl/TUDelft/Over_TU_Delft/Organisatie/regelingen/Studenten%20en%20onderwijs/2021/RG%20BoE%20model%20ENG%202023-2024.pdf.
25 TU Delft Examination Appeals Board Regulations (2007). Examination Appeals Board TU Delft. Reglement College van beroep voor de examens TU Delft. https://filelist.tudelft.nl/TUDelft/Over_TU_Delft/Organisatie/regelingen/rechtsbescherming/CBE_reglement.pdf.
26 Binding guidelines on archiving educational data (2022). Maes, E. & Harting, L. P. https://www.tudelft.nl/teaching-support/didactics/assess/guidelines/archiving.
37 Executive and Management Regulations Delft University of Technology (2014). Executive Board TU Delft. Bestuurs- en beheers reglement TU Delft (BBR). https://www.tudelft.nl/en/about-tu-delft/organisation/regulations/executive-and-management-regulations.
38 Model faculteitsreglement (2017). Executive Board TU Delft. model faculty regulations.
64 Student Charter 2023-2024 (2023). Executive Board TU Delft. Studentenstatuut 2023-2024. https://www.tudelft.nl/en/student/legal-position/education-regulations.
TU Delft policy documents
3 Mulder, A., Baller, T. & Kos, T. (2017). TU Delft Vision on Education.
8 Evaluatiecommmissie Project Studiesucces TU Delft (2017). Onderwijssucces van structuur naar cultuur.
9 TU Delft (2022). TU Delft Vision on Teaching and Learning - 2030 (work in progress).https://www.tudelft.nl/teachingacademy/news/news/previous-newsletters/the-educator-november-2022/vision-on-teaching-and-learning
10 NVAO (2018). Assessment framework for the higher education accreditation system of The Netherlands. https://www.nvao.net/files/attachments/.139/Assessment_Framework_for_the_Higher_Education_Accreditation_System_of_the_Netherlands_2018.pdf.
14 Projectteam Kwaliteitsplan TU Delft (2009). Onderwijskwaliteitsplan TU Delft. https://intranet.tudelft.nl/documents/20147/86040/Onderwijskwaliteitsplan.pdf/d2e74aeb-7233-a39c-9373-870736cbbb00?version=1.0&t=1531315644181.
21 Werkgroep Didactiek (2011). Koersen op Studiesucces. https://docplayer.nl/5964307-Koersen-op-studiesucces.html.
23 Bos, M. & Kariman, F. (2015). Adviesrapport aanvullende fraudepreventie-maatregelen. (2015).
29 Roeser, S. & Copeland, S. (2020). TU Delft Code of Conduct. https://www.tudelft.nl/en/about-tu-delft/strategy/integrity-policy/tu-delft-code-of-conduct.
33 Werkgroep Performancecriteria WP (2008). Performancecriteria bij normal performance voor de Docent.
40 Raijmakers, W. (2022). Verslag Hoofdenoverleg OS d.d. 14 april 2022. (2022).
41 Executive Board TU Delft (2018). Long-term HR Agenda 2018-2024 Impact for and with people.
43 Teaching and Learning Services TU Delft (2023). UTQ Exemption Regulations, filelist.tudelft.nl/Calendar/2023/04 April/UTQExemptionRegulations.pdf.
46 Executive Board TU Delft (2019). Guidance document on career paths with the emphasis on teaching in the position of Associate Professor (UHD) and Full Professor (HL) https://intranet.tudelft.nl/documents/20147/86028/Guidance_document_on_career_paths_with_the_emphasis_on_teaching_in_the_position_of_Associate_and_Full_Professor.pdf/830f2afb-2528-26f2-8af9-7f4b207440a9?version=1.0&t=1565192224851&download=true.
65 Haslinger, I. (2019). TU Delft Strategic Plan Open Science 2020-2024 - Research and Education in the Open Era.
TU Delft manuals
16 Engelbrecht, E., Harting, L. P., Sies, P. & Van Bergen Bravenboer, B. (2022). TU Delft assessment manual. https://www.tudelft.nl/teaching-support/didactics/assess/guidelines/manual.
53 ESA Policy & Implementation TU Delft (2022). Handbook for boards of examiners.
Other
28 Teaching and Learning Services TU Delft (2021). How to create a remote assessment, https://teaching-support.tudelft.nl/remote-assessment/.
34 Harting, L. P., Apikian, G. & Dijkstra, W. P. (2019). Blooms revised taxonomy for learning objectives, https://surfdrive.surf.nl/files/index.php/s/zQ5WUWZ2OzAmWAJ.
42 HR Services TU Delft (2020). Training facilities TU Delft, https://intranet.tudelft.nl/en/group/guest/-/study-costs.
45 HR Services TU Delft (2022). Development days, https://intranet.tudelft.nl/en/-/development-days.
50 HR Services TU Delft (2022). The Learning Hub, https://intranet.tudelft.nl/-/the-learning-hub.
52 Teaching and Learning Services TU Delft (2022). University Teaching Qualification, https://www.tudelft.nl/teaching-support/training-events/university-teaching-qualification-utq-bko.
54 Graduate School TU Delft (2022). T3.A1 | Foundations of Educational Design - Intranet, https://intranet.tudelft.nl/-/t3-a1-foundations-of-educational-design.
56 Graduate School TU Delft (2021). T3.B1 | Coaching Individual Students - Intranet, https://intranet.tudelft.nl/-/t3b1-coaching-individual-students.
57 Teaching and Learning Services TU Delft (2022). Supervision and Assessment Principles, https://www.tudelft.nl/teaching-support/training-events/continuous-professional-development#c1244462.
58 Teaching and Learning Services TU Delft (2022). Teaching Assistant Training, tudelfttls.opleidingsportaal.nl/courses/Teaching Assistant Training.
59 Teaching and Learning Services TU Delft (2022). TLS Training Options, https://tudelfttls.opleidingsportaal.nl/Courses.
60 Teaching and Learning Services TU Delft (2022). Rubrics - Consistent grading of assignments and projects, tudelfttls.opleidingsportaal.nl/courses/Rubrics - Consistent grading of assignments and projects.
61 Centre for Education and Learning (2023). Leiden-Delft-Erasmus Center for Education and Learning, https://www.educationandlearning.nl/home.
62 Teaching and Learning Services TU Delft (2023). Teaching Support, https://teaching-support.tudelft.nl/.
Literature
4 Van Schilt-Mol, T., Sluijsmans, D., Peters, M., De Beer, F. & Jakobs, L. (2016). De touwtjes in handen: toetskwaliteit in het hbo. OnderwijsInnovatie 4, 15-24.
5 Joosten-ten Brinke, D. (2015). Kwaliteit van toetsing onder de loep - Handvatten om de kwaliteit van toetsing in het hoger onderwijs te analyseren, verbeteren en borgen (2 ed.). Garant.
6 Sluijsmans, D., Peeters, A., Jakobs, L. & Weijzen, S. (2012). De kwaliteit van toetsing onder de loep. Tijdschrift OnderwijsInnovatie 4, 17-25.
7 Van Berkel, H. (1999). Zicht op toetsen (1 ed.). Van Gorcum.
11 Erkens, T. (2017). Toetsen met open vragen. In Henk van Berkel, Anneke Bax, & Desirée Joosten-ten Brinke (Eds.), (pp. 145-159). Bohn Stafleu van Loghum. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-368-1679-3_12
13 Wikipedia contributors (2022). PDCA, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=PDCA&oldid=1118077402.
17 Van de Veen, E. (2017). How to assess students through assignments - a guide to creating assignments and rubrics in higher education (2 ed.). Communicatiereeks.
20 Bruijns, V. & Kok, M. (2015). Kwaliteit van toetsbeleid. In Dominique Sluijsmans, Desirée Joosten-ten Brinke, & Tamara van Schilt-Mol (Eds.), Kwaliteit van toetsing onder de loep (1 ed., pp. 93-111). Garant.
24 Murdock, T. B. & Anderman, E. M. (2006). Motivational Perspectives on Student Cheating: Toward an Integrated Model of Academic Dishonesty. Educational Psychologist 41, 129-145. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1207/s15326985ep4103_1
35 van Zijl, E. & Jaspers, M. (2012). Rol examencommissie in de kwaliteitsborging van toetsing. Th&ma 5, 49-52.
36 Jaspers, M. & Zijl van, E. (2014). Samenwerken aan toetskwaliteit in het Hoger Onderwijs. https://edlab.nl/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/Samenwerken-aan-toetskwaliteit.pdf.
39 Carless, D., Salter, D., Yang, M. & Lam, J. (2011). Developing sustainable feedback practices. Studies in higher education 36, 395-407.
63 TU Delft (2018). Impact for a better society. TU Delft Strategic Framework 2018-2024. https://filelist.tudelft.nl/TUDelft/Over_TU_Delft/Strategie/TU%20Delft%20Strategic%20Framework%202018-2024%20%28EN%29.pdf.
Uncategorized References
12 Wijnen, W. H. F. W. et al. (1992). Te doen of niet te doen? Advies over de Studeerbaarheid van onderwijsprogramma's in het hoger onderwijs. http://docplayer.nl/61884849-Te-doen-of-niet-te-doen.html.
15 Expertgroep BKE/SKE in opdracht van de Vereniging Hogescholen (2013). Verantwoord Toetsen en Beslissen in het Hoger Beroeps Onderwijs - een voorstel voor een programma van eisen voor een basis- en seniorkwalificatie examinering (BKE/SKE). https://www.vereniginghogescholen.nl/system/knowledge_base/attachments/files/000/000/330/original/Voorstel_voor_programma_van_eisen_voor_BKE_SKE.pdf?1442920445.
30 Vliegenthart, A. M., Verstand-Bogaert, A. E., Hermans, L. M. L. H. A., Vries, K. G. d. & Korthals, A. H. (2001-2002). Gelijke behandeling op grond van handicap of chronische ziekte - memorie van toelichting. Tweede Kamer 28 169, 40-40.
32 ECIO (2023). 3-step model of accessible assessing and examination in higher education, https://ecio.nl/en/publications/3-step-model-of-accessible-assessing-and-examination-in-higher-education/.
44 (UNL), U. o. t. N. (2022). Collective Labour Agreement for Dutch Universities 1 April 2022–31 March 2023. https://www.caouniversiteiten.nl/en/.
47 Vsnu (2021). UFO/Indelingsinstrument Function family Education and Research - Lecturer / Assistant Professor (A-E).
48 Vsnu (2021). UFO/Indelingsinstrument Function family Education and Research - Lecturer / Senior Lecturer / Associate Professor.
49 Vsnu (2021). UFO/Indelingsinstrument Function family Education and Research - Teacher.
55 Graduate School, T. U. D. (2021). T3.A3 Assessing students and master thesis projects. In. T3.A3 Assessing students and master thesis projects.
-
Figure 1. Assessment building blocks at the TU Delft that determine the assessment quality.
Figure 2. Role of assessment in constructive alignment.
Figure 3. The three TU Delft assessment values and nine quality requirements for assessment.
Figure 4. Assessment building blocks at the TU Delft that determine the assessment quality.
Figure 6. General (summative) assessment cycle TU Delft.
Figure 7. Digital assessment tool landscape TU Delft.
Figure 8. Legal framework of the TU Delft assessment framework and its monitoring.
Figure 9. Schematic organisation at the TU Delft.
Figure 11. Organogram of the central assessment support organisation per service.
-
Table 2: Main assessment characteristics and values.
Table 3: Main timing and fraud prevention/detection characteristics per assessment type.
Table 4. Main required and desired assessment qualifications at TU Delft.
Table 5. Assessment information matrix
Table 6. Reading guide of version 0.9
Table 7. Global TU Delft assessment responsibilities RACI matrix.
Table 8. TU Delft responsibilities for the legal framework for assessment in a RACI matrix.
Table 9. TU Delft responsibilities for the education and assessment process in a RACI matrix.
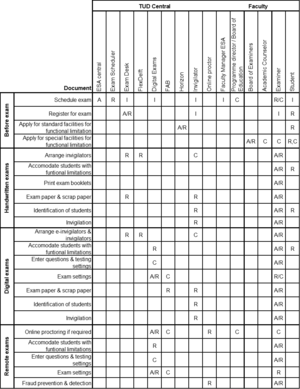
Table 10. TU Delft assessment responsibilities for scheduled exams in a RACI matrix.
-
Type Name Owner Refresh rate/ current version Law (binding) Wet op het hoger onderwijs en wetenschappelijk onderzoek1 (WHW). (Higher Education and Research Act) Minister of Education, Culture and Research No standard rate /
1 January 2023
Framework (binding) Assessment framework for the higher education accreditation system of the Netherlands10 NVAO - /
2018
Regulations (binding) 4TU UTQ regulations51 4TU Education Management Committee - /
18 Nov 2018 -
Type Name Owner Refresh rate / current version Strategic plan (leading) Impact for a better society. TU Delft Strategic Framework 2018-202463 Executive Board 6 years / 2018 Vision (leading) TU Delft Vision on Education3 Executive Board - /
November 2017Regulation (binding) Executive and Management Regulations37
Bestuurs- en beheers reglement TU Delft (BBR)
Executive Board - /
2019
Model regulation (leading) Model Teaching and Examination Regulations2
Model Regels en Richtlijnen van de Examencommissie (RRvE) TU Delft
Executive Board 1 year, large update in 2023 /
2022Model regulation (leading) Joint model BSc / MSc Rules and Guidelines of the Board of Examiners22
Model Regels en Richtlijnen van de ExamencommissieExecutive Board 1 year, large update in 2023 /
2022Regulation (binding) Online Proctored Examination Regulations19
Regeling online proctored tentamen TU DelftExecutive Board - /
November 2020Regulation (binding) Rules and Procedures for Examinations18
Reglement van Orde bij tentamensExecutive Board - /
November 2020Regulation (binding) Examination Appeals Board Regulations25
Reglement College van beroep voor de examens TU DelftExamination Appeals Board - /
20 June 2007Regulation (binding) Student charter64
StudentenstatuutExecutive Board 1 year /
2022Policy (leading) TU Delft Educational Quality Assurance Plan14
Onderwijskwaliteitsplan TU DelftExecutive Board revision expected in 2023 /
Fall 2009Policy (leading) TU Delft Assessment Framework Executive Board 6 years / - (this document) Policy (binding) Binding guidelines for archiving educational data26 Manager Document Management & Archive - / 1 February 2023 Policy (leading) TU Delft strategic plan Open Science 2020-202465 Executive Board - /
2019Format (leading) Model Faculty Regulations38
Model faculteitsreglementExecutive Board - /
July 2017Format (leading) Format annual report board of examiners (Appendix C.2) Executive Board Part of this Assessment Framework (see Appendix C.2) Manual Handbook boards of examiners53
handbook examencommissiesExecutive Board / ESA-P&I & Taskforce Regulations - / 2022 -
Type Name Owner Refresh rate Regulation Faculty Regulations
Faculteitsregelement
Dean - Regulation Rules and Guidelines of the Board of Examiners
Regels en Richtlijnen van de Examencommissie (RRvE)
Board of examiners 1 year Regulation Teaching and Examination Regulations
Onderwijs- en Examenregeling (OER)
Director of education / dean 1 year Policy Faculty assessment policy Director of education 6 years Policy/handbook Faculty quality assurance handbook Dean 0 Policy/procedure Policy on and/or procedure for UTQ exemption Director of education / dean - Annual report Annual report of the board of examiners (to the dean) Board of examiners 1 year Annual report Annual education report of the faculty sss (to the Executive Board) Director of education / dean 1 year
Appendix C. Assessment formats
-
This appendix gives an overview of the most common formats that faculties and programmes use to be in control of the consistency of the assessment on programme, course, and assessment level. The faculty’s assessment experts and educational advisors have access to formats. In addition, the Teaching Support pages offers examples of these formats.
- Formats for programme assessment plans (see 4.2), including:
- Format LO-Final Attainment Levels overview on programme level
- Format to demonstrate the spread in deadlines and assessments
- Formats for the course assessment plans (see 4.3), including:
- Format LO-Final Attainment Levels overview on course level
- Format for assessment matrices on course level (for indicating the assessment method per LO)
- Format for consistency check tables (for courses that consist of a project)
- Formats for individual assessments
- Format for the cover page for examsttt
- Format for exams
- Format for assessment matrices on assessment level
- Format for rubrics
- Format for assessment forms
- Format for consistency check tables (for projects/assignments etc.)
- Format for an assignment/project description that includes minimum information for assignments and projects.
- Formats for programme assessment plans (see 4.2), including:
-
The boards of examiners use the format belowuuu for their annual reports to demonstrate that the board secures the assessment quality of the programme(s), and to extract and compare information between faculties. This enables the TU Delft to detect trends and act upon them. The format provides boards of examiners with some flexibility for their own context.
Format of the annual report of the board of examiners
- Introduction
- General information on the functioning of the Board of Examination
- Composition of the Board of Examiners and, if applicable, of the sub-Boards of Examiners Including schedule of admission (terms of office) and the professionalisations, e.g. UTQ or BoE-training, per member. For example:
Name member Role Board Term Length UTQ BoE-training - Meetings
List of meeting dates / or number of meetings - Information on committees (if applicable), including composition and number of meetings
Example: course assessment committee, graduation work committee - Mandates
Complete list of mandates, or reference to mandate scheme, for e.g.:
- signing degrees
- signing course grade statements
- approving individual exam programmes
- approving composition of graduation assessment committees
- decisions on allowing specific special facilities during exams by the academic councillor in specific cases (if applicable, this needs to be specified)
- writing & signing letters on decisions that were discussed in the BoE meeting
- etc. - Appointment of examiners
Procedure(s) (or reference to procedures(s)) for the appointment, numbers of appointed examiners, number of exemptions on requirements, encountered issues, etc.. - Approvement of composition of graduation assessment committees
Procedure(s) (or reference to procedure(s)) for the approvement of graduation assessment committees. - Analysis of trends and consequences for policy / regulations
Include recommendations, if necessary.
- Composition of the Board of Examiners and, if applicable, of the sub-Boards of Examiners Including schedule of admission (terms of office) and the professionalisations, e.g. UTQ or BoE-training, per member. For example:
- Quality of degrees
- Number of degrees, preferably plotted over time
- Propedeuse degrees (if applicable, including the number of cum laude)
- Bachelor degrees (including the number of cum laude)
- Hounours' programme bachelor
- Master degrees (including the number of cum laude) per track, plus free programme
- Endorsements (if still applicable)
- Honours' programme master
- Analysis of trends and consequences for policy / regulations
(e.g. cum laude policy) Include recommendations, if necessary.
- Number of degrees, preferably plotted over time
- Quality of assessment programme
- Structural activitities of the BoE to ensure the quality of the assessment programme
Yearly analysis of each assessment programme, request for this overview, etc. - Analysis of trens and consequences for policy / regulations
Include recommendations, if necessary.
- Structural activitities of the BoE to ensure the quality of the assessment programme
- Quality of graduation projects
- Structural activities of the BoE to ensure quality of graduation projects
- Analysis of trends and consequences for polocy / regulations
Include recommendations, if necessary.
- Quality of assessment in courses
- Structural activities of the BoE to ensure quality of graduation projects
- Analysis of trends and consequences for polocy / regulations
Include recommendations, if necessary.
- Fraud
- Prevent, policy
- Numbers per type of fraud (plagiarism, other)
- Analysis of trends and consequences for policy / regulations
Include recommendations, if necessary.
- Individual requests
- Numbers
this includes number pres:- Changes to the examination programme:
- Exemptions
- Free minors
- Requests for special facilities during examinations or for other assessment types
Due to disabilities, chronic disease, special individual circumstances, or not being able to be physically present in the examination place. - Electives
- Course abroad
- Requests by lecturers to change the assessment compared to the study guide description (during the academic year)
- Changes to the examination programme:
- Analysis of trends and consequences for polocy / regulations
Include recommendations, if necessary.
- Numbers
- Appeal cases
- Numbers per types
- Analysis of trends and consequences for polocy / regulations
Include recommendations, if necessary.
- Regulations
- Rules & Guidelines of the Board of Examination (establishment)
Date of establishment of the Rules & Guidelines, list of changes compared to last year, including brief explanation - Teaching and Examination Regulations and their addenda (advice)
List of advice on the TER and whether or not these advices have been processed.
- Rules & Guidelines of the Board of Examination (establishment)
- Assessment policy
- Advice on the faculty’s (or programme’s) assessment policy
- Contribution/advice to specific assessment policy topics
List of points to which the Board contributed or on which the Board wrote an advice, to whom it was given, and a description of the advice
- Reflection on previous year and plans for the next year
- Reflection on and list of plans of previous year
List points of attention - Next year: Plans of the Board of Examiners
An outline of points of attention - Next year: Recommendations and requests to the Dean
- Conclusion
- Reflection on and list of plans of previous year
Appendix D. Assessment responsibilities (RACI)
In this appendix, so called RACI matrices (a responsibility assignment matrix) describe the assessment responsibilities. These matrices indicate per task who is accountable (finally responsible) for this task (indicated by ‘A’), who is responsible (R) for conducting task for the accountable person, who needs to be consulted on this task (C), and who should be informed of the outcome (I). If a letter is between brackets (), this means that this person is only responsible, consulted, or informed, in situations that require this (as opposed to always). Hence ‘R’ means that this person carries out a task related to the activity, not that they are responsible, since this is indicated by an ‘A’.
The right column indicates what the sources are of the accountability and of the consultancy requirements (if available). The responsible (R) and informed (I) people are based on current (or desired) processes. NB. ‘consulted’ can imply both that this body needs to give consent, or that they need to be consulted.
Appendix E. Organisational differences between faculties
This appendix gives an overview of the main organisational differences between faculties that are relevant for assessment.
-
Depending on the faculty, ‘programme director’ can be called ‘director of studies’ in some faculties (e.g. AE, AS, EEMCS, CEG). See the assessment policy of the faculty for the actual organisation.
-
In addition, at IDE, AE and ME, an ‘educational management team’ (EMT, names may vary) is accountable for all programmes, instead of each individual programme director for their own programme. These EMTs consists of the following people (see the Faculty Regulations and WHW):
- IDE: Director of Education, all programme directors, head of ESA, student. This is called the ‘Board of Education' (BoE, opleidingsdirectie).
- AE: both programme directors (one of them is also Director of Education), student (EMT, opleidingsbestuur)
- ME: Director of Education, programme directors, head of ESA, student
Other faculties may also have EMT’s, but they do not have the same power as the EMTs that are mentioned above. -
Usually, it is the programme director who negotiates with the department heads on teaching staff. However, according to their Faculty Regulations, at IDE, EEMCS and ME, this responsibility is divided as follows:
1) IDE: the Director of Education has this responsibility
2) EEMCS: the educational management (Director of Education, programme directors, and the Director of Interfaculty Education) share this responsibility
3) ME: shared responsibility of the programme directors and Director of Education -
Most faculties have a single board of examiners that are responsible for all programmes. At AE, AS and EEMCS, there are subboards of examiners per programme, in addition to the central board of examiners. In these faculties, the subboards of examiners appoint examiners, instead of the board of examiners.
-
In some faculties like TPM, ESA hires and trains student assistants (SAs) centrally to support lecturers in e.g. creating digital assessment. In other faculties like CEG, it is the department of the responsible lecturer of the course that hires SAs. Since TLS provides SA training per faculty, CEG’s ESA arranges the SA training.
-
Term Description adaptive assessment Test that adapts the degree of difficulty and/or subject to the students’ individual abilities while the test is being taken. adaptive question Within a question, the next subquestion depends on the correctness of the answer to the previous subquestion. The lecturer can set the assessment tool to show the exact same subquestion for a limited number of times until the student gives the correct answer, or reaches the maximum number of tries, in which case the tool shows the student the correct answer, which the student can use in the next subquestion. anonymous scoring Assessors score student work without access to the student’s identity. answer key Correct answer to a closed-ended question. This can also be an equation, or a numerical answer, depending on the question type. answer model Combination of model answer plus scoring guide: indicates per partially correct answer and per part of a correct answer how many points will be awarded and indicates how many points will be subtracted for specific errors. Example for mcq: A: 1 point, B: ½ point, C: 0 points, D: 0 points. Example for open question: calculation step 1: +2 points, calculation step 2: +3 points, step 3: +1 point, no units: -1 point. archiving securely storing data until reaching the retention period. Securely implies restricting access, making the data findable, and ensuring that the data cannot be changed, archived securely Data and metadata are stored safely and is preferably no longer changeable so that later it is certain that this is the original version. assessment Educational activities during which individual students demonstrate how well they master the learning objectives of a course, and during which their performance is measured. This information is shared with students to steer and/or evaluate their learning. Examples: projects, exams. assessment activity Activity that a student does during an assessment. In constructively aligned courses, this matches the learning objectives. assessment agreement Part of the programme assessment plan that consists of agreements for all assessments in that specific programme. assessment competence To what extent an employee of the TU Delft who participates in an assessment process is able to perform their assessment tasks in such a way that it leads to good quality assessment. assessment criteria Aspects of a product or process on which a student are assessed on, for example during a project. assessment matrix Blueprint of an assessment for an exam: A matrix that indicates for all individual subquestions and their maximum scores what learning objective (rows) they assess on which level of the used taxonomy (columns). assessment method Examples: written exam, oral exam, project, report, presentation, etc. assessment mode Whether the assessment is administered under physical supervision of an examiner and/or invigilator (i.e., in an exam hall/room), whether the assessment is administered via the internet (i.e., remote), or whether the assessment is hybrid (a combination of on-campus and online). course assessment plan Overview of the assessments in a course. Its goal is to demonstrate how the learning objectives of a course are assessed in a valid, reliable, transparent way that stimulates learning. It includes the main characteristics of the course like contribution to final grade (0% - 100%), regulations for retake / addition, feedback on the assessment, what learning objectives are assessed per assessment, approximate week planning of deadlines and assessments, allowed use tools & information during the assessment, assessment tooling, how the final grade represents the performance of an individual student and how the learning objectives contribute to the programme’s intended learning outcomes. programme assessment plan Overview of the assessment in a programme. Its goal is to demonstrate how the final attainment levels (FALs) of the programme are assessed in the combination of the programme’s courses in a valid way. It includes an overview of what courses contribute to what FALs and what assessment forms are used to assess these. assessment tool Digital tool (e.g. software, online tool) in which parts of the assessment cycle are conducted or supported. Examples: designing assessments, administering assessments, doing exams as a student, proctoring/invigilating, handing in student work, scoring student work, providing feedback, test result analysis, grade calculating, grade communication, students reviewing and discussing graded work and grades, grade administration, evaluating assessment, plagiarism check, online proctoring, etc. assessor Person who scores or gives feedback to student work or student performance. author Someone who composes the test and who compiles/develops (sub)questions, either individually or in collaboration with other authors. binding recommendation on the continuation of studies (BSA) Binding advice to individual students on the continuation of whether they can continue their studies. Given at the end of the first year of the Bachelor. Dutch: Bindend studieadvies (BSA). Bloom level One of the following 6 levels in the adapted cognitive taxonomy of Bloom: understand, apply, analyse, evaluate, create (adapted cognitive taxonomy). See here34. blueprint Schematic representation of an assessment in a matrix. For exams, this is an assessment matrix; for projects/assignments/etc. a consistency check table is more common.
Etymology: a blueprint of a building was a white-on-blue technical drawing of e.g. a building in the early 20th century.bring-your-own-device assessment Assessment in an exam room during which students perform the digital exam on their own laptop. Typically requires extra security measures. BYOD calibration session Session during which assessors who grade the same assignment proof-grade (example) student work and discuss differences in scores and feedback to improve the quality and consistency of their grading and feedback. closed-ended question Question to which the answer is given by selecting one or multiple items from a limited number of options. Examples: multiple choice, multiple select, matching, selecting a number from a limited range, selecting part of a picture, etc. Closed-ended questions could lead to a correct answer without prior knowledge by randomly choosing an answer option, which implies the need for guessing correction. combination test Test that is composed of two separate tests with a separate score. An example being one part of a test with closed questions and another part with open questions. consistency check table Overview of a project (or large assignment) which indicates per learning objective (rows) which related criteria (content of the cells) are assessed formatively and summatively per (intermediate or final) deliverable(s) or process(es) (columns). constructive alignment Design principle for courses and programmes to stimulates student learning. In constructively aligned courses, learning objectives, learning activities and assessment activities are aligned. In constructively aligned programmes, final attainments, learning objectives and assessment types are aligned. course Coherent unit of study within a programme that includes learning activities and formative assessments to help students master the learning objectives, and summative assessment(s) of which the results express how well individual students have succeeded in this. After passing the summative assessment, students receive the ECs that correspond to the course. Some courses consist fully or partially of a project.
Other term used in some programmes: module.
course coordinator The lecturer who is responsible for the course as a whole. Terminology used in study guide: ‘responsible lecturer’. course grade course grade cover page Front page of a paper exam that the student reads and that contains general information and general instructions. criterion Aspect on which students’ deliverables or the process of creating them will be graded. cut-off score Score, that a student needs for a grade of 6.0 (minimum pass score). Dutch: cesuur degree audit the test in which the BoEx determines whether the student as successfully completed all examinations in the courses of the degree programme (WHW art. 7.10). If so, the EB awards the student with the relevant BSc or MSc degree (WHW art. 7.10a sub 1). Dutch: examen (not to be confused with exam=tentamen). degree program List of courses that the board of examiners approved and that an individual student needs to complete in order to obtain the desired degree. There are standard degree programmes, and individual / free degree programmes, which the board of examiners explicitly has to approve. descriptor Description of how students’ deliverables or the process of creating them looks like at a specific level for a specific criterion in a rubric. See rubric. device Device on which a student takes the test (terms used in other places: computer, workstation). digital exam Written exam input type during which students answer exam questions with the help of a computer. Digital Exams TU Delft service that supports lecturers in the process of scheduled digital on-campus and remote written exams. drawing tool Tool within an assessment tool that allows to draw a picture, graph, or diagram. Some drawing tools may allow for automatic grading of student input in the tool. educational period Period during which courses run. The basic educational periods are four quarters (Q1 to Q4) and a summer period for retakes (Q5). See https://www.tudelft.nl/en/student/education/academic-calendar. e-invigilator Invigilator for a digital exam who helps examiners and students with administrative and technical issues. Examples: add unregistered students to the exam, help students to continue on another computer and provide compensatory time in case of computer issues. EvaSys System that administers questionnaires for course evaluations to students, and processes the outcome of these evaluations into reports. exam Scheduled summative written test that students take during a specific exam timeslot on a specific day. Examples: written exam, oral exam.
NB1: in the TER and R&G, all types of summative assessments are called ‘examinations’ (tentamens), including assignments and projects.
NB2: ‘exam’ should not be confused with the Dutch word ‘examen’, which is ‘degree audit’ (see ‘degree audit’).
exam timeslot Timeslot during which students can take the test. exam period Period during which most exams take place. Every educational period has an exam period in week x.9 and x.10 (or only x.10, x being the number of the quarter, see ‘educational period’), and some programmes have an exam period for midterms around week x.5. See https://www.tudelft.nl/en/student/education/academic-calendar. Few tests take place outside these periods. examination Formal word for ‘assessment’. Can refer to any type of assessment. Examination Appeals Board (EAB) TU Delft appeals board that processes and decides on appeal cases by students on assessment (see WHW art. 7.61, sub 1). This includes course grades given by examiners (students cannot appeal against partial grades until the final course grade has been communicated) and decisions of the board of examiners. The BoEx can make decisions on e.g. complaints by individual or groups of students on an assessment, or on requests for an extra assessment opportunity. The working method of the EAB is described in the Examination Appeals Board Regulations. Dutch: College van Beroep voor de Examens, CBE. examiner Member of the teaching staff who is appointed examiner by the board of examiners and who is responsible (alone or with colleagues) for the content and process of the examination of a course, including the responsibility for grading the tests. feedback Structured information for students on their performance and possibilities for improvement, based on the quality of a student product or process. Feedback is structured per assessment criterion and/or learning objective and used in a follow-up learning activity or assessment. Feedback can be given by peers, teaching staff or by the student themself (via self-assessment). final attainment (level) List of achievements of graduates that describe what graduates of a programme are able to do after successfully completing the programme. Synonym 1 (used during accreditations): intended learning outcome / ILO.
Synonym 2: exit qualification
Abbreviation: FAL.
See: intended learning outcome. Abbreviation: ILO.final grade The final grade of a course. Synonym: course grade. formative assessment Assessment that does not influence the grade of a course and is meant to give students feedback on how well they currently master the learning objectives and what steps they still need to take to improve before the summative assessment at end of the course. Formative assessment counts as such 1) if the assessment is at the level of the learning objectives, 2) if the performance of students during the activity does not count for the course grade or passing the course and if the activity is voluntary, 3) if students receive structured feedback on the assessment criteria or learning objectives, and 4) if students are able and stimulated to use the feedback in consecutive learning activities and summative assessment. fraud ‘any act or omission by a student that makes it fully or partially impossible to properly assess the knowledge, insight and skill of that student or another student’22 free riding a form of fraud in group work where one student of the group is not contributing on terms of time investment or output. Synonym: ‘piggy backing’ functional application manager A functional application manager is responsible within an organisation for the optimal functioning of one or more information systems. Not only do they ensure the continuity of the systems, but they also fulfil a supporting role regarding the users. In that sense, functional management forms the connection between ICT and business operations. graduation MSc or BSc graduation. guessing correction Average score by randomly guessing the answer to closed-ended questions. GDPR General Data Protection Regulation, see https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2016/679/oj. GPA Grade point average: Weighted average of all numerical grades of an individual student in a programme, rounded to two decimals, excluding results from Honours Programme courses. grade Description of student performance on a test, which is based on the score using a score-grade conversion (synonyms: mark (Australia, US)). hybrid assessment Test that consists of a digital part (via a device) and a paper-based, handwritten part. inspection Possibility for students to inspect/review their graded work and discuss objections to the score with the examiner. Also: student inspection. institutional audit “An institutional audit is a periodic, external, and independent assessment of the internal quality assurance in place at an institution. Internal quality assurance comprises both the quality culture and the internal quality assurance system of an institution. The audit serves to verify that the institution’s internal quality assurance system, in interconnection with its quality culture, safeguards the realisation of its individual vision of good education.”page 6 in 10 intended learning outcome See final attainment level (FAL). Abbreviation: ILO. invigilator Someone who supervises the exam for the detection of irregularities and fraudulent behaviour on campus. knock-out criterion A criterion that has a minimum level that needs to be met in order for the student to receive feedback and/or a grade. learning activities Activities that a student performs during a course in order to train the learning objectives. learning objectives List of achievements that describe what students are able to do after successfully completing the course. They describe the ultimate but feasible level of the course.
Synonym at other universities: learning outcome, intended learning outcome. Abbreviation: LOs. Singular: LOLMS Learning Management System. At TU Delft, this is currently Brightspace. lockdown browser Prevents students to access other applications than the browser needed to access the test, and that limits the access of the browser to the test, and to whitelisted pages. Also called secure browser. mark Noun: Can mean either score (points for an exam question) or grade (converted from the score), depending on country of origin. Not used at TU Delft to prevent confusion.
Verb: evaluating student work as an assessor or examiner, while attributing points per question or assessment criterion and/or adding feedback. Synonyms: grade, score, evaluate, review.
meta data Characteristics of (sub)questions in an assessment tool that either the lecturer attributes (for example learning objective, topic, difficulty, peer review status), or that the assessment tool attributes based on historical data (for example history of use in tests, parent, p-value, RiR-value). midterm in the context of exams: An exam in the middle of the educational period, which typically covers the first half of the course and counts for up to 50% of the course grade.
in the context of graduation projects: an interim evaluation / feedback moment during the project, typically halfway the project. Depending on the faculty/programme, this can include a decision on continuation of the project.
in the context of accreditation / quality assurance: an internal evaluation halfway between accreditations (3 years after the accreditation) to check the progress of the programme in terms of the NVAO standards.
model answer Correct answer. In some cases, multiple correct answers exist. The one that is handed to the students is called the model answer. The model answer could also contain multiple correct answers or answer routes. multiple choice question Question type that requires students to pick one out of a number of proposed answers. See also: multiple select question, closed-ended question. multiple select question Question type that requires students to pick one or more out of a number of proposed answers. See also: multiple choice question, closed-ended question. online proctoring Online proctoring is only possible for closed-book tests if it is not possible to assess the course using open-book tests, i.e., in case of knowledge exams or exams on math questions for which the answers can be achieved using symbolic computation software (e.g., Maple, Mathematica, MATLAB) or online tools. Permission from the board of examiners is requiredvvv open book test Historically, this meant that students could bring the course’s book (and sometimes a list of other books) to the exam hall. In case of remote tests, ‘open book’ implies access to the internet as well. Contact with other people is prohibited. open-ended question Question to which the set of correct answers is not given by selecting an answer from a limited number of options (see closed-ended question). In case the answer is not predictable, manual scoring requires the help of a rubric or answer model. oral check Fraud detection method conducted after an unsupervised assessment, during which examiners question individual student from a (quasi) random sample of the entire student population on their submitted work. The goal is to evaluate the likelihood that the student was the actual author of the submitted work. Osiris student information system in which student register for exams and in which lecturers communicate course grades and in some programmes also partial grades. p-value Normalized average score per subquestion or question. Formula: p-value = average score / maximum score. Example: p=1.0 implies all students received maximum score. p=0 scored on average 0 points. p can be negative if minus points are awarded. However, this is not recommended.
The p-value is a measure for the ‘difficulty’ of a question, to which it is inversely proportional: the more difficult a question is, the lower it p-value.
NB: This is a different p-value from the one in statistical context.
paper exam Exam during which the student writes the answers to questions and/or assignments on paper. parameterized question (sub)question in which both the question and correct answer depend on defined parameters or variables (numerical and algebraic) that are stated in the question description. The parameter values are determined randomly for each realization of the question. partial grade Grade for an assessment within a course. The weighted average of al partial grades forms the course grade. In most faculties, partial grades have a minimum value in order to pass the course. Partial grades can consist of subgrades (see subgrade). passing grade The minimum grade that is required to pass a course. At TU Delft, this is 6.0 after rounding the final course grade to halves. PDCA cycle Plan-do-check-adjust cycle; a way of improving processes or products iteratively. For assessment, it implies that the examiner plans a good assessment (Plan), administers, and grades the assessment (Do), checks the quality of the assessment based on test result analysis and/or student input (Check), and adjusts the next assessment based on the findings (Adjust). peer review Process during which other lecturers review individual questions or entire tests and give feedback on the question-and-answer model. peer reviewer Lecturer who reviews questions or the test before the test is administered to students. practice exercise Questions like the ones that can be found in standard textbooks. Goal is to train students to master the level of the learning objectives. These questions help students to master the learning objectives by gradually increasing in complexity. Unlike formative assessments, they typically, are not (yet) at the level of the learning objectives. Also called ‘scaffolding questions’. proctor Invigilator who invigilates video recordings of remote exams. programme Educational programme (combination of courses and graduation project). Students receive a MSc degree or BSc degree after successful completion of a programme. question Single question to which the student needs to formulate or otherwise indicates an answer/answers. A question can consist of a coherent set of sub questions. (Terms used in other places: item, assignment) question bank Digital collection of questions (which can consist of sub questions) that can be used for a test. Questions can be labelled with characteristics, like metadata and keywords. (Term used in other places: item bank) question pool A set of similar questions of comparable difficulty, from which the assessment tool randomly selects a question to create unique exams. RACI matrix Matrix that indicates per tasks or process (rows) who (columns) is accountable (A) for this task/process, who is Responsible (i.e. who needs to take action), who can be held Accountable, who needs to be Consulted, and who needs to be Informed. remote assessment Assessment that would normally take place on campus that take place online due to exceptional circumstances such as corona. Requires special fraud prevention measures and possibly approval from the board of examiners and/or educational management. repair option Possibility for students who did not pass a course in one go, to pass the course that year. Only applicable for courses with other assessment forms than exams. Example: assignments, projects, lab work, etc. The repair option does not require redoing the entire assessment; This only requires delivering an updated version or doing a smaller repair assignment. Typically, a maximum grade applies. result Result of a test or course that is communicated to the student. The result typically is a grade between 1 and 10, rounded to decimals, but a result can also be ‘pass’ or ‘fail’. If a student does not show at an exam, the examinator can register ‘NV’ (no show), which is technically not a result. responsible lecturer See ‘course coordinator’ retake / resit Second opportunity in a year to sit an exam. Primarily meant for students who missed the main exam due to circumstances, but open to all students. retention period How long e.g. a document should continue to exist. See also: archiving period. random Generate one or more (quasi)random values within a range that is predefined, striving for a uniform occurrence over the range. This promotes that all values will occur with about the same frequency, even in small groups. Rir-value Correlation between the student scores for a certain (sub)question, and the total student score for all other (sub)questions. Low Rir-values indicate that otherwise good performing students (on this assessment) score poorly on this question. Rit-value Correlation between the student scores for a certain (sub)question, and the total student scores. Low Rit-values indicate that otherwise good performing students (on this assessment) score poorly on this question. The Rir-value is more accurate. rubric Matrix used to determine the score per criterion that the students are assessed on. For all criteria (rows), the requirements for each level (columns) are described as descriptors in the cells of the matrix. Either the criteria are weighted and the points per level are the same for all criteria, or the points per level differ between criteria. Used to score essay-like questions as well as larger assignments/projects. safeguarding Making sure that something happens, without having to do it yourself. Synonym: securing, guaranteeing. Dutch: borgen. score-grade transformation Determining the grades from the students’ total scores. Typically implemented as a single linear equation (y = a∙x + b) or two linear equations (one for scores below the cut-off score and one for scores above the cut-off score). scoring Process of determining individual student scores on (sub)questions in a test (terms used in other places: marking, grading). scoring guide Indicates in an answer model how many points should be added for each correct part of the student answer and subtracted per error/omission. section Group of questions in a test that belong together. Sometimes used for dividing the test into different topics, or types of questions. Assessment tools typically can apply specific rules per section (terms used in other places: part, block). secure browser Software on the student’s device that limits the access to internet, other applications, or peripherals with the goal of preventing a student from accessing forbidden information during a test. Also called lockdown browser. securing Making sure that something happens, without having to do it yourself. Synonyms: safeguarding, guaranteeing. Dutch: borgen. selection list Official national document that dictates how long documents resulting from educational processes like assessment need to be archived and whether these need to be destroyed after this period. Most assessment related documents fall under process 54, which is abbreviated as ‘SL proc. 54’. Section 3.4 is dedicated to the archiving of assessment and degree related documents. Official name: ‘Selection List Universities and University Medical Centres 2020’ (Selectielijst Universiteiten en Universitair Medische Centra 2020). standard feedback Feedback to students that is connected to the answer model. In case of certain errors or correct steps, students receive standard feedback. Example: ‘You forgot to square c in E = m∙c2.’ STEM Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics. stem The stem of a question is the first part, that precedes the question and the instructions (in the case of open questions) or the answer options (in the case of multiple-choice questions). structured feedback Feedback that is structured per applicable LO or assessment criterion. The term is used as the opposite of ‘unstructured feedback’, in which not all LOs or criteria are systematically assessed. student assistant (SA) Student who has a job in a university where they assist employees. In case their job description is focussed on education, they are called ‘student assistants’. In case their job description is focussed on support (e.g. at TLS), they are called ‘support assistants’ (SAs), and otherwise ‘teaching assistants’ (TAs). However, the latter term is also in use for non-students like PhD students and postdocs. student information system (SIS) In SIS, students can register for assessments and view their study results. At the TU Delft: Osiris. (student) review Possibility for students to review/inspect their graded work and discuss objections to the score with the examiner. student work Something that was created by a student. Example: homework, assignments, report, exam, etc. Typically, teaching staff provides feedback to student work, and/or grades student work. support assistant (SA) student who has a job at TLS to support lecturers in their teaching, for example by providing help on the use of tools. subgrade One of the subgrades within a partial grade or within an assessment. Example 1: an exam can have a subgrade for open-ended questions and a subgrade for closed-ended questions, of which the weighted average is the exam grade. Example 2: a partial grade for lab work can consist of several subgrades per lab day. Subgrade should not be confused with partial grades of a course (see partial grade). subquestion Part of a question, e.g., question 1b, to which a student needs to formulate or otherwise indicate an answer. summative assessments Any assessment that contributes to the final result (grade or pass/fail) of a course. This includes mandatory activities in the course. Teaching & Learning Services Organization that supports lecturers of the entire TU Delft with training, advise, and support. teaching assistant (TA) Someone who has a job to assist a lecturer in their teaching. In the context of assessment, teaching assistants (TAs) can help entering questions in an assessment tool, review questions, monitor and help during the test, and help scoring student answers in the assessment tool. They do everything under close supervision of the examiner. Often used as a synonym of student assistant, although in some faculties like Applied Science, also PhD’s and postdocs can be teaching assistants. teaching week Teaching weeks are weeks during which educational activities take place. They are numbered p.w where p is the period number (periods 1-4 are the regular periods; period 5 is the summer period that is only used for resits which lasts either 9 or 10 weeks, depending on the year), and w is the week number (1-10). Week 1.1 is the first or second week of September. See https://www.tudelft.nl/en/student/education/academic-calendar technical application manager Employee who deals with the installation, approval, and the process of making the technical systems and infrastructure operational and keeping them that way. test An assessment of (a part of) the learning objectives of a course. It can have the form of a written exam, a try-out exam, a midterm, or homework assignments that can be summative or formative, but not a project or presentation. Practice exercises like in standard textbooks are not considered tests. test duration Allowed maximum duration during which students can take the test.
test result analysis Overview of quality indicators on sub question, question, and test level (e.g., p-value, maximum score, correlation with rest score, Cronbach’s alpha). Goal: to determine learning objective achievement of the group, and to determine indicators to improve the answer model/scoring guide before publishing the grades. total score Sum of all scores in a test for a single student. UTQ exemption Exemption from the obligation to obtain UTQ qualification, based on an assessment to determine that the candidate has a level equivalent to the UTQ level. This can be based on an equivalent certificate, or an assessment of an educational portfolio. Each faculty has their own UTQ exemption procedure43. See 6.1. answer key Correct answer to a closed-ended question. This can also be an equation, or a numerical answer, depending on the question type. answer model Combination of model answer plus scoring guide: indicates per partially correct answer and per part of a correct answer how many points will be awarded and indicates how many points will be subtracted for specific errors. Example for mcq: A: 1 point, B: ½ point, C: 0 points, D: 0 points. Example for open question: calculation step 1: +2 points, calculation step 2: +3 points, step 3: +1 point, no units: -1 point. archiving securely storing data until reaching the retention period. Securely implies restricting access, making the data findable, and ensuring that the data cannot be changed, archived securely Data and metadata are stored safely and is preferably no longer changeable so that later it is certain that this is the original version. assessment Educational activities during which individual students demonstrate how well they master the learning objectives of a course, and during which their performance is measured. This information is shared with students to steer and/or evaluate their learning. Examples: projects, exams. assessment activity Activity that a student does during an assessment. In constructively aligned courses, this matches the learning objectives. assessment agreement Part of the programme assessment plan that consists of agreements for all assessments in that specific programme. assessment competence To what extent an employee of the TU Delft who participates in an assessment process is able to perform their assessment tasks in such a way that it leads to good quality assessment. assessment criteria Aspects of a product or process on which a student are assessed on, for example during a project. assessment matrix Blueprint of an assessment for an exam: A matrix that indicates for all individual subquestions and their maximum scores what learning objective (rows) they assess on which level of the used taxonomy (columns). assessment method Examples: written exam, oral exam, project, report, presentation, etc. assessment mode Whether the assessment is administered under physical supervision of an examiner and/or invigilator (i.e., in an exam hall/room), whether the assessment is administered via the internet (i.e., remote), or whether the assessment is hybrid (a combination of on-campus and online). course assessment plan Overview of the assessments in a course. Its goal is to demonstrate how the learning objectives of a course are assessed in a valid, reliable, transparent way that stimulates learning. It includes the main characteristics of the course like contribution to final grade (0% - 100%), regulations for retake / addition, feedback on the assessment, what learning objectives are assessed per assessment, approximate week planning of deadlines and assessments, allowed use tools & information during the assessment, assessment tooling, how the final grade represents the performance of an individual student and how the learning objectives contribute to the programme’s intended learning outcomes. programme assessment plan Overview of the assessment in a programme. Its goal is to demonstrate how the final attainment levels (FALs) of the programme are assessed in the combination of the programme’s courses in a valid way. It includes an overview of what courses contribute to what FALs and what assessment forms are used to assess these. assessment tool Digital tool (e.g. software, online tool) in which parts of the assessment cycle are conducted or supported. Examples: designing assessments, administering assessments, doing exams as a student, proctoring/invigilating, handing in student work, scoring student work, providing feedback, test result analysis, grade calculating, grade communication, students reviewing and discussing graded work and grades, grade administration, evaluating assessment, plagiarism check, online proctoring, etc. assessor Person who scores or gives feedback to student work or student performance. author Someone who composes the test and who compiles/develops (sub)questions, either individually or in collaboration with other authors. binding recommendation on the continuation of studies (BSA) Binding advice to individual students on the continuation of whether they can continue their studies. Given at the end of the first year of the Bachelor. Dutch: Bindend studieadvies (BSA). Bloom level One of the following 6 levels in the adapted cognitive taxonomy of Bloom: understand, apply, analyse, evaluate, create (adapted cognitive taxonomy). See here34. blueprint Schematic representation of an assessment in a matrix. For exams, this is an assessment matrix; for projects/assignments/etc. a consistency check table is more common.
Etymology: a blueprint of a building was a white-on-blue technical drawing of e.g. a building in the early 20th century.bring-your-own-device assessment Assessment in an exam room during which students perform the digital exam on their own laptop. Typically requires extra security measures. BYOD calibration session Session during which assessors who grade the same assignment proof-grade (example) student work and discuss differences in scores and feedback to improve the quality and consistency of their grading and feedback. closed-ended question Question to which the answer is given by selecting one or multiple items from a limited number of options. Examples: multiple choice, multiple select, matching, selecting a number from a limited range, selecting part of a picture, etc. Closed-ended questions could lead to a correct answer without prior knowledge by randomly choosing an answer option, which implies the need for guessing correction. combination test Test that is composed of two separate tests with a separate score. An example being one part of a test with closed questions and another part with open questions. consistency check table Overview of a project (or large assignment) which indicates per learning objective (rows) which related criteria (content of the cells) are assessed formatively and summatively per (intermediate or final) deliverable(s) or process(es) (columns). constructive alignment Design principle for courses and programmes to stimulates student learning. In constructively aligned courses, learning objectives, learning activities and assessment activities are aligned. In constructively aligned programmes, final attainments, learning objectives and assessment types are aligned. course Coherent unit of study within a programme that includes learning activities and formative assessments to help students master the learning objectives, and summative assessment(s) of which the results express how well individual students have succeeded in this. After passing the summative assessment, students receive the ECs that correspond to the course. Some courses consist fully or partially of a project.
Other term used in some programmes: module.
course coordinator The lecturer who is responsible for the course as a whole. Terminology used in study guide: ‘responsible lecturer’. course grade course grade cover page Front page of a paper exam that the student reads and that contains general information and general instructions. criterion Aspect on which students’ deliverables or the process of creating them will be graded. cut-off score Score, that a student needs for a grade of 6.0 (minimum pass score). Dutch: cesuur degree audit the test in which the BoEx determines whether the student as successfully completed all examinations in the courses of the degree programme (WHW art. 7.10). If so, the EB awards the student with the relevant BSc or MSc degree (WHW art. 7.10a sub 1). Dutch: examen (not to be confused with exam=tentamen). degree program List of courses that the board of examiners approved and that an individual student needs to complete in order to obtain the desired degree. There are standard degree programmes, and individual / free degree programmes, which the board of examiners explicitly has to approve. descriptor Description of how students’ deliverables or the process of creating them looks like at a specific level for a specific criterion in a rubric. See rubric. device Device on which a student takes the test (terms used in other places: computer, workstation). digital exam Written exam input type during which students answer exam questions with the help of a computer. Digital Exams TU Delft service that supports lecturers in the process of scheduled digital on-campus and remote written exams. drawing tool Tool within an assessment tool that allows to draw a picture, graph, or diagram. Some drawing tools may allow for automatic grading of student input in the tool. educational period Period during which courses run. The basic educational periods are four quarters (Q1 to Q4) and a summer period for retakes (Q5). See https://www.tudelft.nl/en/student/education/academic-calendar. e-invigilator Invigilator for a digital exam who helps examiners and students with administrative and technical issues. Examples: add unregistered students to the exam, help students to continue on another computer and provide compensatory time in case of computer issues. EvaSys System that administers questionnaires for course evaluations to students, and processes the outcome of these evaluations into reports. exam Scheduled summative written test that students take during a specific exam timeslot on a specific day. Examples: written exam, oral exam.
NB1: in the TER and R&G, all types of summative assessments are called ‘examinations’ (tentamens), including assignments and projects.
NB2: ‘exam’ should not be confused with the Dutch word ‘examen’, which is ‘degree audit’ (see ‘degree audit’).
exam timeslot Timeslot during which students can take the test. exam period Period during which most exams take place. Every educational period has an exam period in week x.9 and x.10 (or only x.10, x being the number of the quarter, see ‘educational period’), and some programmes have an exam period for midterms around week x.5. See https://www.tudelft.nl/en/student/education/academic-calendar. Few tests take place outside these periods. examination Formal word for ‘assessment’. Can refer to any type of assessment. Examination Appeals Board (EAB) TU Delft appeals board that processes and decides on appeal cases by students on assessment (see WHW art. 7.61, sub 1). This includes course grades given by examiners (students cannot appeal against partial grades until the final course grade has been communicated) and decisions of the board of examiners. The BoEx can make decisions on e.g. complaints by individual or groups of students on an assessment, or on requests for an extra assessment opportunity. The working method of the EAB is described in the Examination Appeals Board Regulations. Dutch: College van Beroep voor de Examens, CBE. examiner Member of the teaching staff who is appointed examiner by the board of examiners and who is responsible (alone or with colleagues) for the content and process of the examination of a course, including the responsibility for grading the tests. feedback Structured information for students on their performance and possibilities for improvement, based on the quality of a student product or process. Feedback is structured per assessment criterion and/or learning objective and used in a follow-up learning activity or assessment. Feedback can be given by peers, teaching staff or by the student themself (via self-assessment). final attainment (level) List of achievements of graduates that describe what graduates of a programme are able to do after successfully completing the programme. Synonym 1 (used during accreditations): intended learning outcome / ILO.
Synonym 2: exit qualification
Abbreviation: FAL.
See: intended learning outcome. Abbreviation: ILO.final grade The final grade of a course. Synonym: course grade. formative assessment Assessment that does not influence the grade of a course and is meant to give students feedback on how well they currently master the learning objectives and what steps they still need to take to improve before the summative assessment at end of the course. Formative assessment counts as such 1) if the assessment is at the level of the learning objectives, 2) if the performance of students during the activity does not count for the course grade or passing the course and if the activity is voluntary, 3) if students receive structured feedback on the assessment criteria or learning objectives, and 4) if students are able and stimulated to use the feedback in consecutive learning activities and summative assessment. fraud ‘any act or omission by a student that makes it fully or partially impossible to properly assess the knowledge, insight and skill of that student or another student’22 free riding a form of fraud in group work where one student of the group is not contributing on terms of time investment or output. Synonym: ‘piggy backing’ functional application manager A functional application manager is responsible within an organisation for the optimal functioning of one or more information systems. Not only do they ensure the continuity of the systems, but they also fulfil a supporting role regarding the users. In that sense, functional management forms the connection between ICT and business operations. graduation MSc or BSc graduation. guessing correction Average score by randomly guessing the answer to closed-ended questions. GDPR General Data Protection Regulation, see https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2016/679/oj. GPA Grade point average: Weighted average of all numerical grades of an individual student in a programme, rounded to two decimals, excluding results from Honours Programme courses. grade Description of student performance on a test, which is based on the score using a score-grade conversion (synonyms: mark (Australia, US)). hybrid assessment Test that consists of a digital part (via a device) and a paper-based, handwritten part. inspection Possibility for students to inspect/review their graded work and discuss objections to the score with the examiner. Also: student inspection. institutional audit “An institutional audit is a periodic, external, and independent assessment of the internal quality assurance in place at an institution. Internal quality assurance comprises both the quality culture and the internal quality assurance system of an institution. The audit serves to verify that the institution’s internal quality assurance system, in interconnection with its quality culture, safeguards the realisation of its individual vision of good education.”page 6 in 10 intended learning outcome See final attainment level (FAL). Abbreviation: ILO. invigilator Someone who supervises the exam for the detection of irregularities and fraudulent behaviour on campus. knock-out criterion A criterion that has a minimum level that needs to be met in order for the student to receive feedback and/or a grade. learning activities Activities that a student performs during a course in order to train the learning objectives. learning objectives List of achievements that describe what students are able to do after successfully completing the course. They describe the ultimate but feasible level of the course.
Synonym at other universities: learning outcome, intended learning outcome. Abbreviation: LOs. Singular: LOLMS Learning Management System. At TU Delft, this is currently Brightspace. lockdown browser Prevents students to access other applications than the browser needed to access the test, and that limits the access of the browser to the test, and to whitelisted pages. Also called secure browser. mark Noun: Can mean either score (points for an exam question) or grade (converted from the score), depending on country of origin. Not used at TU Delft to prevent confusion.
Verb: evaluating student work as an assessor or examiner, while attributing points per question or assessment criterion and/or adding feedback. Synonyms: grade, score, evaluate, review.
meta data Characteristics of (sub)questions in an assessment tool that either the lecturer attributes (for example learning objective, topic, difficulty, peer review status), or that the assessment tool attributes based on historical data (for example history of use in tests, parent, p-value, RiR-value). midterm in the context of exams: An exam in the middle of the educational period, which typically covers the first half of the course and counts for up to 50% of the course grade.
in the context of graduation projects: an interim evaluation / feedback moment during the project, typically halfway the project. Depending on the faculty/programme, this can include a decision on continuation of the project.
in the context of accreditation / quality assurance: an internal evaluation halfway between accreditations (3 years after the accreditation) to check the progress of the programme in terms of the NVAO standards.
model answer Correct answer. In some cases, multiple correct answers exist. The one that is handed to the students is called the model answer. The model answer could also contain multiple correct answers or answer routes. multiple choice question Question type that requires students to pick one out of a number of proposed answers. See also: multiple select question, closed-ended question. multiple select question Question type that requires students to pick one or more out of a number of proposed answers. See also: multiple choice question, closed-ended question. online proctoring Online proctoring is only possible for closed-book tests if it is not possible to assess the course using open-book tests, i.e., in case of knowledge exams or exams on math questions for which the answers can be achieved using symbolic computation software (e.g., Maple, Mathematica, MATLAB) or online tools. Permission from the board of examiners is requiredvvv open book test Historically, this meant that students could bring the course’s book (and sometimes a list of other books) to the exam hall. In case of remote tests, ‘open book’ implies access to the internet as well. Contact with other people is prohibited. open-ended question Question to which the set of correct answers is not given by selecting an answer from a limited number of options (see closed-ended question). In case the answer is not predictable, manual scoring requires the help of a rubric or answer model. oral check Fraud detection method conducted after an unsupervised assessment, during which examiners question individual student from a (quasi) random sample of the entire student population on their submitted work. The goal is to evaluate the likelihood that the student was the actual author of the submitted work. Osiris student information system in which student register for exams and in which lecturers communicate course grades and in some programmes also partial grades. p-value Normalized average score per subquestion or question. Formula: p-value = average score / maximum score. Example: p=1.0 implies all students received maximum score. p=0 scored on average 0 points. p can be negative if minus points are awarded. However, this is not recommended.
The p-value is a measure for the ‘difficulty’ of a question, to which it is inversely proportional: the more difficult a question is, the lower it p-value.
NB: This is a different p-value from the one in statistical context.
paper exam Exam during which the student writes the answers to questions and/or assignments on paper. parameterized question (sub)question in which both the question and correct answer depend on defined parameters or variables (numerical and algebraic) that are stated in the question description. The parameter values are determined randomly for each realization of the question. partial grade Grade for an assessment within a course. The weighted average of al partial grades forms the course grade. In most faculties, partial grades have a minimum value in order to pass the course. Partial grades can consist of subgrades (see subgrade). passing grade The minimum grade that is required to pass a course. At TU Delft, this is 6.0 after rounding the final course grade to halves. PDCA cycle Plan-do-check-adjust cycle; a way of improving processes or products iteratively. For assessment, it implies that the examiner plans a good assessment (Plan), administers, and grades the assessment (Do), checks the quality of the assessment based on test result analysis and/or student input (Check), and adjusts the next assessment based on the findings (Adjust). peer review Process during which other lecturers review individual questions or entire tests and give feedback on the question-and-answer model. peer reviewer Lecturer who reviews questions or the test before the test is administered to students. practice exercise Questions like the ones that can be found in standard textbooks. Goal is to train students to master the level of the learning objectives. These questions help students to master the learning objectives by gradually increasing in complexity. Unlike formative assessments, they typically, are not (yet) at the level of the learning objectives. Also called ‘scaffolding questions’. proctor Invigilator who invigilates video recordings of remote exams. programme Educational programme (combination of courses and graduation project). Students receive a MSc degree or BSc degree after successful completion of a programme. question Single question to which the student needs to formulate or otherwise indicates an answer/answers. A question can consist of a coherent set of sub questions. (Terms used in other places: item, assignment) question bank Digital collection of questions (which can consist of sub questions) that can be used for a test. Questions can be labelled with characteristics, like metadata and keywords. (Term used in other places: item bank) question pool A set of similar questions of comparable difficulty, from which the assessment tool randomly selects a question to create unique exams. RACI matrix Matrix that indicates per tasks or process (rows) who (columns) is accountable (A) for this task/process, who is Responsible (i.e. who needs to take action), who can be held Accountable, who needs to be Consulted, and who needs to be Informed. remote assessment Assessment that would normally take place on campus that take place online due to exceptional circumstances such as corona. Requires special fraud prevention measures and possibly approval from the board of examiners and/or educational management. repair option Possibility for students who did not pass a course in one go, to pass the course that year. Only applicable for courses with other assessment forms than exams. Example: assignments, projects, lab work, etc. The repair option does not require redoing the entire assessment; This only requires delivering an updated version or doing a smaller repair assignment. Typically, a maximum grade applies. result Result of a test or course that is communicated to the student. The result typically is a grade between 1 and 10, rounded to decimals, but a result can also be ‘pass’ or ‘fail’. If a student does not show at an exam, the examinator can register ‘NV’ (no show), which is technically not a result. responsible lecturer See ‘course coordinator’ retake / resit Second opportunity in a year to sit an exam. Primarily meant for students who missed the main exam due to circumstances, but open to all students. retention period How long e.g. a document should continue to exist. See also: archiving period. random Generate one or more (quasi)random values within a range that is predefined, striving for a uniform occurrence over the range. This promotes that all values will occur with about the same frequency, even in small groups. Rir-value Correlation between the student scores for a certain (sub)question, and the total student score for all other (sub)questions. Low Rir-values indicate that otherwise good performing students (on this assessment) score poorly on this question. Rit-value Correlation between the student scores for a certain (sub)question, and the total student scores. Low Rit-values indicate that otherwise good performing students (on this assessment) score poorly on this question. The Rir-value is more accurate. rubric Matrix used to determine the score per criterion that the students are assessed on. For all criteria (rows), the requirements for each level (columns) are described as descriptors in the cells of the matrix. Either the criteria are weighted and the points per level are the same for all criteria, or the points per level differ between criteria. Used to score essay-like questions as well as larger assignments/projects. safeguarding Making sure that something happens, without having to do it yourself. Synonym: securing, guaranteeing. Dutch: borgen. score-grade transformation Determining the grades from the students’ total scores. Typically implemented as a single linear equation (y = a∙x + b) or two linear equations (one for scores below the cut-off score and one for scores above the cut-off score). scoring Process of determining individual student scores on (sub)questions in a test (terms used in other places: marking, grading). scoring guide Indicates in an answer model how many points should be added for each correct part of the student answer and subtracted per error/omission. section Group of questions in a test that belong together. Sometimes used for dividing the test into different topics, or types of questions. Assessment tools typically can apply specific rules per section (terms used in other places: part, block). secure browser Software on the student’s device that limits the access to internet, other applications, or peripherals with the goal of preventing a student from accessing forbidden information during a test. Also called lockdown browser. securing Making sure that something happens, without having to do it yourself. Synonyms: safeguarding, guaranteeing. Dutch: borgen. selection list Official national document that dictates how long documents resulting from educational processes like assessment need to be archived and whether these need to be destroyed after this period. Most assessment related documents fall under process 54, which is abbreviated as ‘SL proc. 54’. Section 3.4 is dedicated to the archiving of assessment and degree related documents. Official name: ‘Selection List Universities and University Medical Centres 2020’ (Selectielijst Universiteiten en Universitair Medische Centra 2020). standard feedback Feedback to students that is connected to the answer model. In case of certain errors or correct steps, students receive standard feedback. Example: ‘You forgot to square c in E = m∙c2.’ STEM Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics. stem The stem of a question is the first part, that precedes the question and the instructions (in the case of open questions) or the answer options (in the case of multiple-choice questions). structured feedback Feedback that is structured per applicable LO or assessment criterion. The term is used as the opposite of ‘unstructured feedback’, in which not all LOs or criteria are systematically assessed. student assistant (SA) Student who has a job in a university where they assist employees. In case their job description is focussed on education, they are called ‘student assistants’. In case their job description is focussed on support (e.g. at TLS), they are called ‘support assistants’ (SAs), and otherwise ‘teaching assistants’ (TAs). However, the latter term is also in use for non-students like PhD students and postdocs. student information system (SIS) In SIS, students can register for assessments and view their study results. At the TU Delft: Osiris. (student) review Possibility for students to review/inspect their graded work and discuss objections to the score with the examiner. student work Something that was created by a student. Example: homework, assignments, report, exam, etc. Typically, teaching staff provides feedback to student work, and/or grades student work. support assistant (SA) student who has a job at TLS to support lecturers in their teaching, for example by providing help on the use of tools. subgrade One of the subgrades within a partial grade or within an assessment. Example 1: an exam can have a subgrade for open-ended questions and a subgrade for closed-ended questions, of which the weighted average is the exam grade. Example 2: a partial grade for lab work can consist of several subgrades per lab day. Subgrade should not be confused with partial grades of a course (see partial grade). subquestion Part of a question, e.g., question 1b, to which a student needs to formulate or otherwise indicate an answer. summative assessments Any assessment that contributes to the final result (grade or pass/fail) of a course. This includes mandatory activities in the course. Teaching & Learning Services Organization that supports lecturers of the entire TU Delft with training, advise, and support. teaching assistant (TA) Someone who has a job to assist a lecturer in their teaching. In the context of assessment, teaching assistants (TAs) can help entering questions in an assessment tool, review questions, monitor and help during the test, and help scoring student answers in the assessment tool. They do everything under close supervision of the examiner. Often used as a synonym of student assistant, although in some faculties like Applied Science, also PhD’s and postdocs can be teaching assistants. teaching week Teaching weeks are weeks during which educational activities take place. They are numbered p.w where p is the period number (periods 1-4 are the regular periods; period 5 is the summer period that is only used for resits which lasts either 9 or 10 weeks, depending on the year), and w is the week number (1-10). Week 1.1 is the first or second week of September. See https://www.tudelft.nl/en/student/education/academic-calendar technical application manager Employee who deals with the installation, approval, and the process of making the technical systems and infrastructure operational and keeping them that way. test An assessment of (a part of) the learning objectives of a course. It can have the form of a written exam, a try-out exam, a midterm, or homework assignments that can be summative or formative, but not a project or presentation. Practice exercises like in standard textbooks are not considered tests. test duration Allowed maximum duration during which students can take the test.
test result analysis Overview of quality indicators on sub question, question, and test level (e.g., p-value, maximum score, correlation with rest score, Cronbach’s alpha). Goal: to determine learning objective achievement of the group, and to determine indicators to improve the answer model/scoring guide before publishing the grades. total score Sum of all scores in a test for a single student. UTQ exemption Exemption from the obligation to obtain UTQ qualification, based on an assessment to determine that the candidate has a level equivalent to the UTQ level. This can be based on an equivalent certificate, or an assessment of an educational portfolio. Each faculty has their own UTQ exemption procedure43. See 6.1. -
English Dutch assessment toetsing of toets assessment criteria beoordelingscriteria assignment (grote) opdracht, vaak bestaande uit meerdere oefeningen. board of education opleidingsdirectie board of examiners examencommissie board of studies opleidingscommissie cut-off score cesuur degree programme examenprogramma director of education directeur onderwijs director of studies opleidingsdirecteur (also: programme director) examiner examinator exercise (kleine) opdracht/oefening intended learning objective eindterm invigilator surveillant lecturer docent learning objective leerdoel programme opleidingsprogramma programme director opleidingsdirecteur (also: director of studies) Rules of Procedures for Examinations reglement van orde bij tentamens (RvO) -
Acronym Description ME Faculty of Mechanical Engineering (Werktuigbouwkunde, ME) 4TU federation of four Universities of Technology (TU) in the Netherlands ABE Architecture and the Built Environment (Bouwkunde, BK) ACT Academic Career Track AE Faculty of Aerospace Engineering (Luchtvaart- en Ruimtevaarttechniek, LR) AS Faculty of Applied Sciences (Technische Natuurwetenschappen, TNW) AT Assessment Taskforce BBR Bestuurs- en BeheersReglement (Executive and Management Regulations, EMR) BoEd Board of Education (opleidingsdirectie) BoEx Board of Examiners BSc Bachelor of Science BSA Binding recommendation on the continuation of studies BYOD Bring Your Own Device CBE Commissie voor Beroep van de Examens, Examination Appeal Board (EAB) CEG Civil Engineering and Geosciences (Civiele Techniek & Geowetenschappen, CiTG) CvB Executive Board (CvB) DE Digital Exams DEE Digital Excellence for Education EAB Examination Appeals Board (see CBE) EB Executive Board (CvB) EC European Credit (studiepunt) ECTS European Credit Transfer System (studiepuntuitwisselingssysteem), sometimes incorrectly instead of EC ED Exam Desk EEMCS Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics & Computer Science (Elektrotechniek, Wiskunde & Informatica, EWI) EMR Executive and Management Regulations (Bestuurs- en beheersreglement TU Delft, BBR) EMT Educational Management Team ESA Education & Student Affairs ESA-SPA Education & Student Affairs – Study Programme Administration FA Final attainment FAB Functional Application Manager FAL Final Attainment Level, also called ILO FoA Focus on Assessment FR Faculty Regulations FSC Faculty Student Council FTE full-time equivalent GPA Grade Point Average HERA Higher Education and Research Act (Wet op het Hoger onderwijs en Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek, WHW). We use ‘WHW’ because there is no English version available. HOS Meeting Heads of ESA (Hoofden Onderwijs & Studentenzaken) HR Human Resources IDE Faculty of Industrial Design Engineering (Industrieel Ontwerpen, IO) ILO Intended Learning Outcome, FAL is more common in Delft IM Information Management IM-SPA Information Management - Security, Privacy and Architecture LO Learning Objective mcq Multiple Choice Question MSc Master of Science MT Management Team ODO Meeting Directors of Education (Overleg Directeuren Onderwijs) O&S Education and Student Affairs, ESA (Onderwijs- & Studentenzaken) PDCA Plan-do-check-adjust or plan-do-check-act (see, PDCA cycle) PhD Doctoral student (promovendus) P&I Policy and Implementation (department of ESA) R&D Result & Development Cycle R&G Rules & Guidelines of the Board of Examiners RACI Responsible, accountable, communicate, inform RPE Rules of Procedures for Examinations (Reglement van Orde bij tentamens, RvO) RvO Reglement van Orde bij tentamens (see RPE) SA Student Assistant (general), or Support Assistant (at TLS) SAP Supervision and Assessment Principles (course) SC Student Council SEQ Senior Examination Qualification (course) SL Selection List Universities and University Medical Centers 2020 (Selectielijst Universiteiten en Universitair Medische Centra 202027) SPA Study Programme Administration SSO Single sign-on T3.A1 Foundations of Educational Design (Graduate School course) T3.A3 Assessing students and master thesis projects (Graduate School course) T3.B1 Coaching Individual Students and Project Groups (Graduate School course) TA Teaching Assistant TAB Technical Application Manager TER Teaching and Examination Regulations TIL Transport, Infrastructure and Logistics TLS Teaching & Learning Services TPM Faculty of Technology, Policy, and Management (Techniek, Bestuur en management, TBM) TLS Teaching & Learning Services UNL Universities of The Netherlands (previously VSNU) UTQ University Teaching Qualification (training programme) Wgbh/cz Act on Equal Treatment of the grounds of Disability or Chronic Illness, Wet gelijke behandeling op grond van handicap of chronische ziekte WHW Higher Education and Research Act (Wet op het Hoger onderwijs en Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek, WHW). Sometimes abbreviated as ‘HERA’
sss) Mentioned in model Faculty Regulations art. 7.8 sub 1 and art. 9.3 sub e
ttt) A checklist with required content of the cover page can be found in the TU Delft assessment manual16.
uuu) The format was improved by the Taskforce Regulations (werkgroep regelgeving) and P&I, after which the chairs of the boards of examiners were consulted in their meeting in May 2023.
vvv) See https://www.tudelft.nl/en/student/my-study-me/education/courses-and-examinations/examinations/online-proctored-examination-regulation