Subspace Predictive Repetitive Control
Background
As wind turbines are being upscaled to raise their cost-effectiveness, active load alleviation methods are required to limit the costs associated with the maintenance of these turbines. One method to achieve this that is already implemented in a growing number of wind turbines, is individual pitch control (IPC). In IPC, each blade is pitched cyclically to oppose the repetitive loads on the blades. In this project, we work on a data-driven control stategy called Subspace Predictive Repetitive Control (SPRC). SPRC combines online subspace identification with the implementation of a repetitive control law.
Goal/ objective
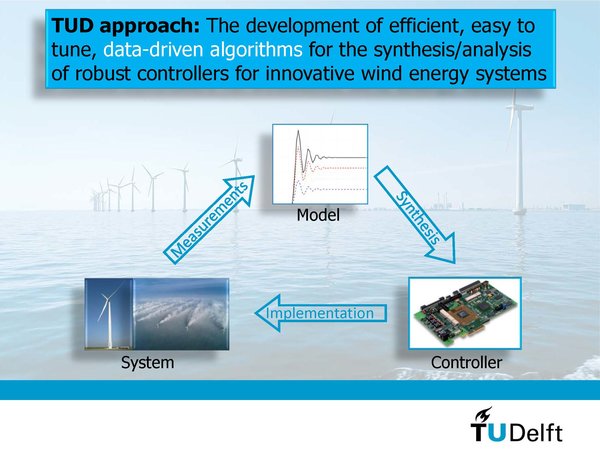
The goal of data-driven control is to develop efficient, easy to tune algorithms for the synthesis and analysis of robust controllers for innovative wind energy systems. Furthermore, we aim to develop adaptive controllers that have the ability to adopt to changes in the system dynamics.
Work programme
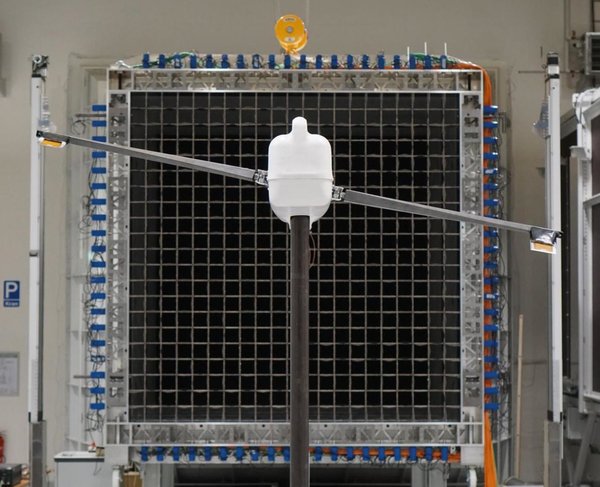

To achieve the objectives mentioned above, state-of-the-art control needs to be combined with real-world tests and/or high-fidelity simulations. The developed control techniques can be evaluated using:
(i) Wind tunnel tests on scaled wind turbines;
(ii) High-fidelity models such as the OpenFAST turbine model.
At the same time, the SPRC algorithm can be developed by implementing basis functions to reduce the dimensionality of the problem, or by adding constraints to the optimization problem.
Outcome
The research will lead to robust, efficient data-driven control algorithms that are applicable on a wide range of real-time systems. Scaled experiments can be used to show the effectiveness of the method in reducing repetitive loads and thus increasing the lifetime of the system.
Project team members

- ir. Joeri Frederik
- dr. ir. Jan-Willem van Wingerden
Keywords
Subspace identification, Predictive Control, Repetitive Control, Wind Turbine, Individual Pitch Control, Adaptive control, Data-driven Control
Sponsored by:
This research is made possible by the EU Horizon 2020 project INNWIND.EU (see www.innwind.eu).
Partners
Oldenburg University