What is Citizen Science (CS)?
Citizen science actively involves the public in scientific research that generates new knowledge or understanding, and thus has the potential to bring together science, policy makers, and society as a whole in an impactful way.
Citizen science explained
-
Citizen science actively involves the public in scientific research that generates new knowledge or understanding, and thus has the potential to bring together science, policy makers, and society in an impactful way. Citizen science is a flexible concept which can be adapted and applied within many situations and disciplines, and represents a range of approaches and historical practices for public participation in scientific research. Citizen scientists can participate in many stages of the scientific process, from data collection and mapping, through data interpretation and analysis, to publication and dissemination of results.
-
Citizen science does not just engage citizens with research, it also gives them an active role in academic research. Researchers invite citizens for an active contribution to their research. Giving citizens an active role can contribute to mutual trust and understanding.
-
You can collaborate with citizens to different degrees, depending on what fits your goals and research. Broadly, we distinguish for ‘levels’ of citizen engagement, with increasingly bigger roles and responsibilities for the citizens involved.
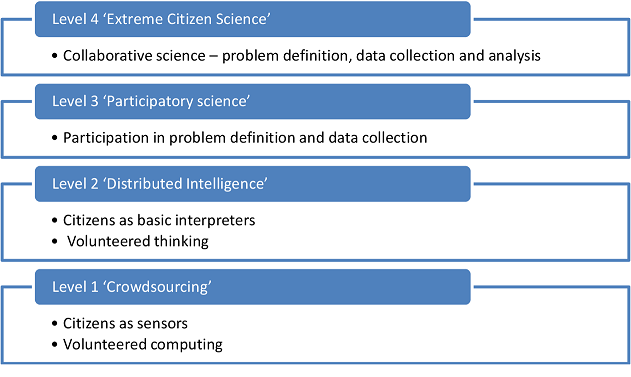
Levels of participation and engagement in citizen science projects. © Haklay (2013), Doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4587-2_7
Benefits of citizen science
Citizen science is a relatively new concept within science, but is getting more and more popular as part of research projects. It has multiple benefits:
- It is an efficient way to collect and process data. A group of citizen scientists that each do a little work, can collect a lot more data in a much smaller timeframe than any researcher or research-group can gather in the same timeframe.
- Citizen scientist can collect from places that can be hard to reach for researchers, like backyards or schoolyards.
- Citizen science is a great opportunity to test new technologies or innovations on a larger scale.
What does a citizen science project entail
A citizen science project involves a certain group of citizens in one or more phases of research, sometimes in collaboration with a knowledge institution, like a university, but not necessarily. This can happen at smaller and larger scales and a suitable and interested group of volunteers is assembled. This group will have an active contribution to one or more parts of the project. The job that these citizen scientists do can be collecting data, categorizing it, or doing part of the analysis. In some cases they are cocreating the research question or methodology in collaboration with the main researcher. In some cases there is a prior training or workshop, so that volunteers are sufficiently prepared.