This project aims to find promising ways to fit a technical principle, which is being developed at the TU Delft, in the context of Visceral Leishmaniasis(VL). During the project, the team visited VL endemic regions in Eastern Uganda and North-Western to understand the context. To apply the technical principle in the context of VL, seven scenarios were created. After evaluation, the most promising scenarios have been selected based on the feasibility of the technical principle, the contextual fit and the local need. The following video explains the project in detail.
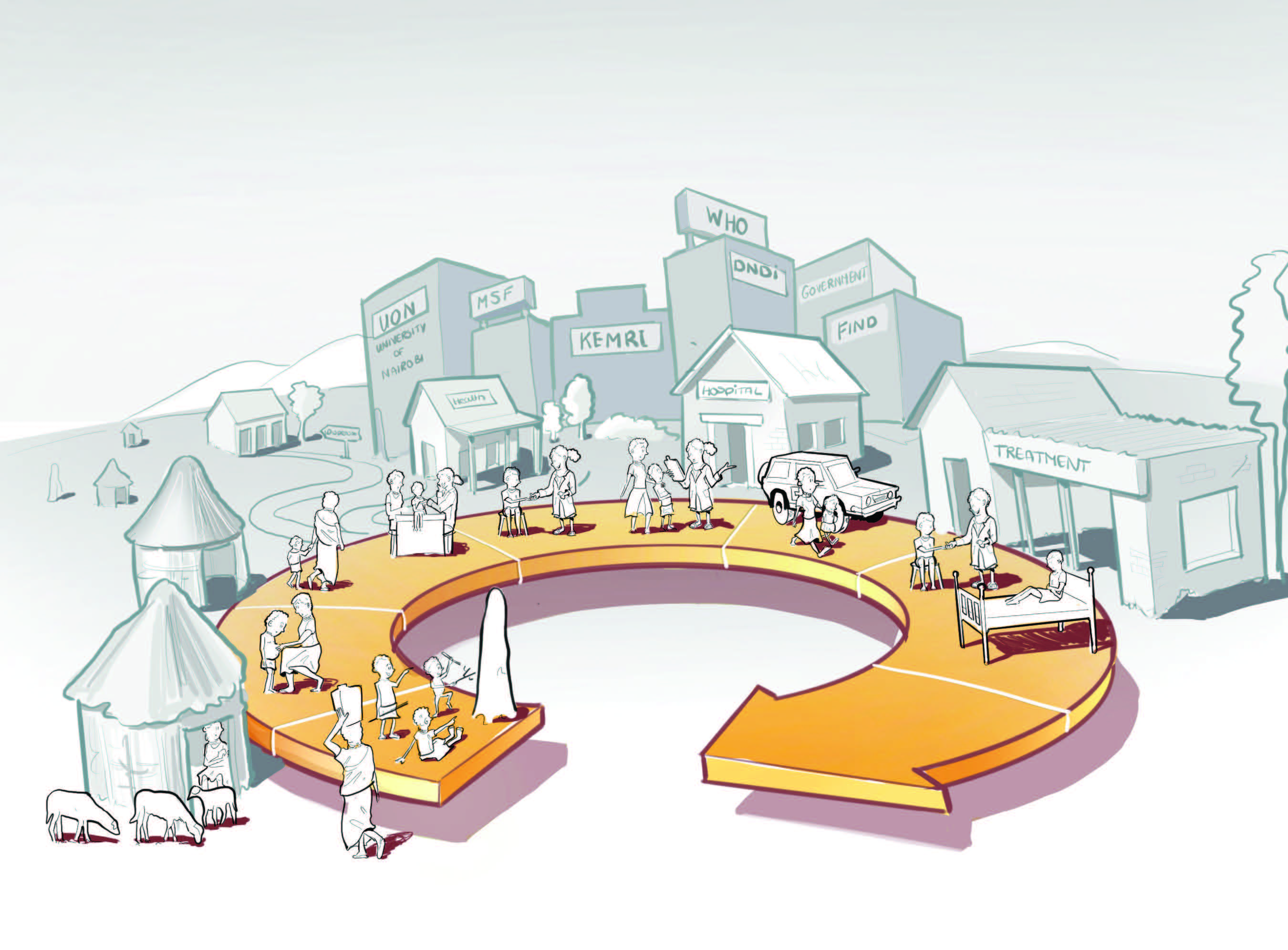
Case study in East Africa
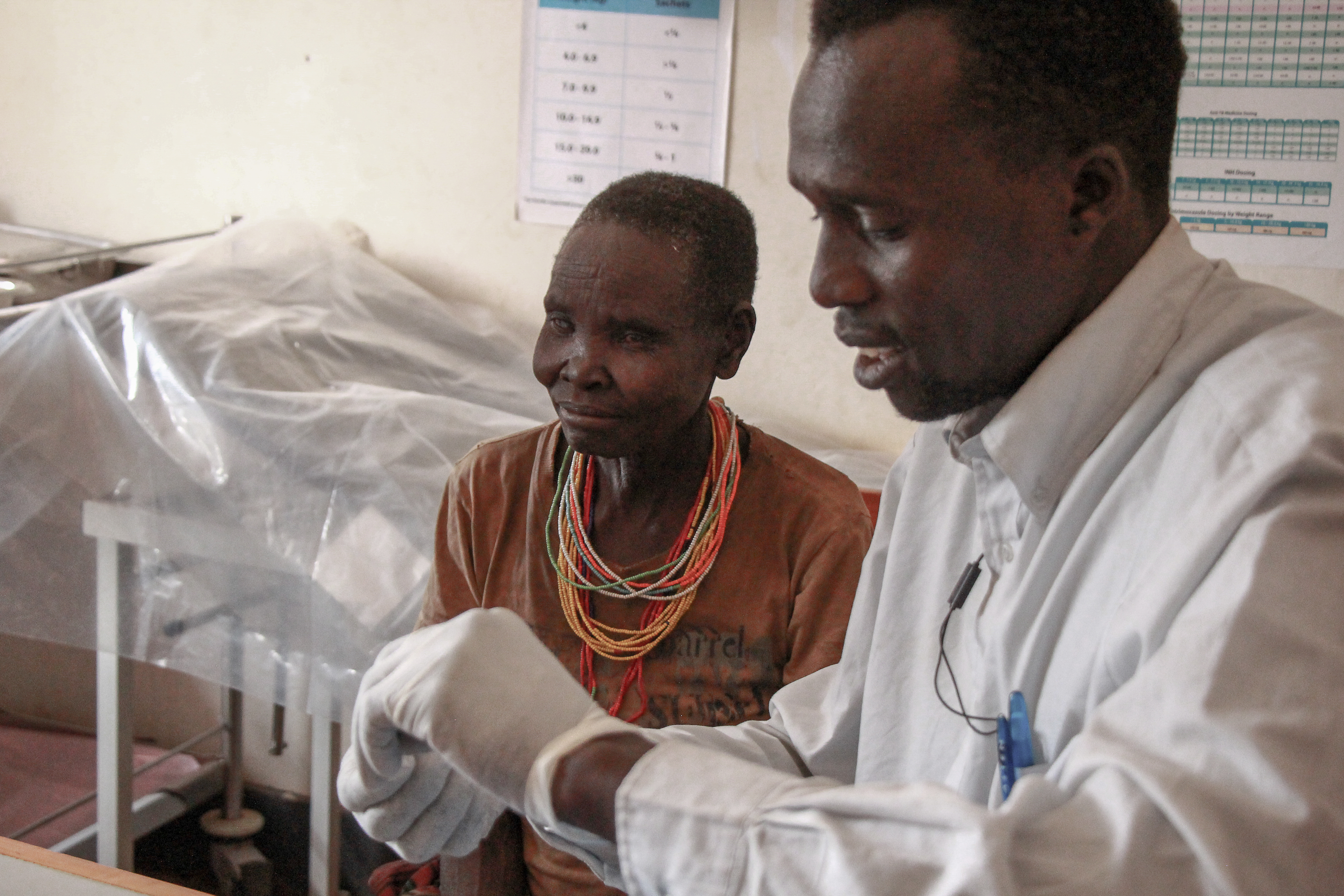
VL is a parasitic disease which is endemic in several parts in the world including East Africa. The disease is strongly related to poverty and mainly persists in remote and poor areas where health care services are limited. VL affects the internal organs and is fatal if untreated. There are many barriers complicate access VL diagnostics and treatment, such as the limited number of facilities, large distances, lack of trained staff and low index of suspicion by health care workers. VL is often misdiagnosed as the symptoms of VL are similar to many other diseases. In addition, current diagnostic practices have limitations in their performance (unreliable), especially in East Africa. More reliable diagnostic practices require more advanced tools and skills which are not available in most VL endemic areas.
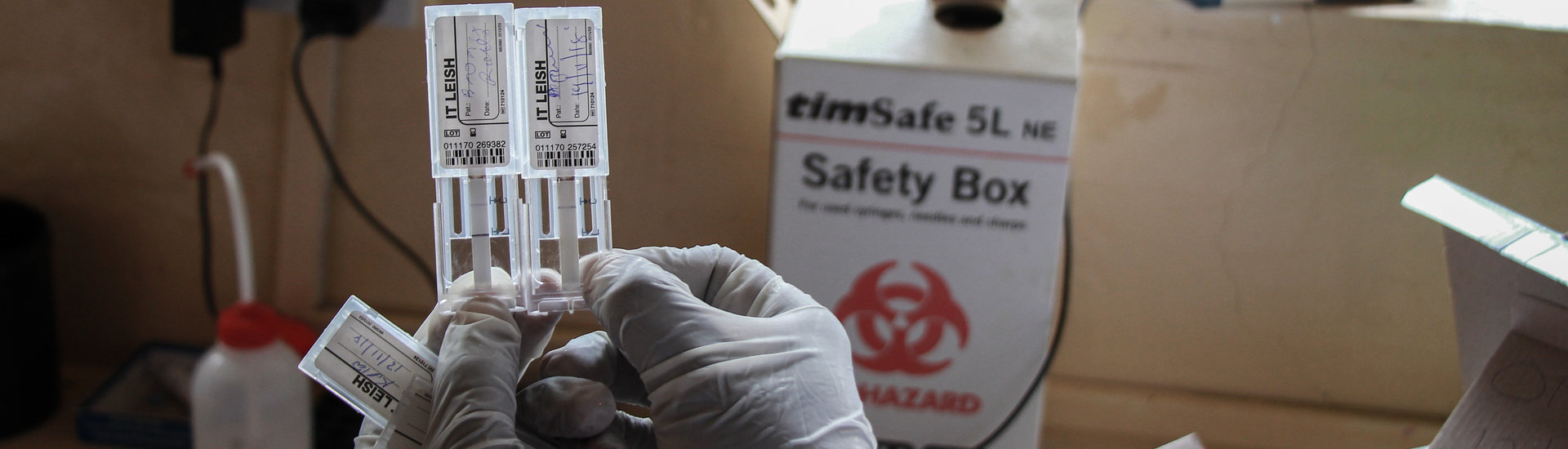
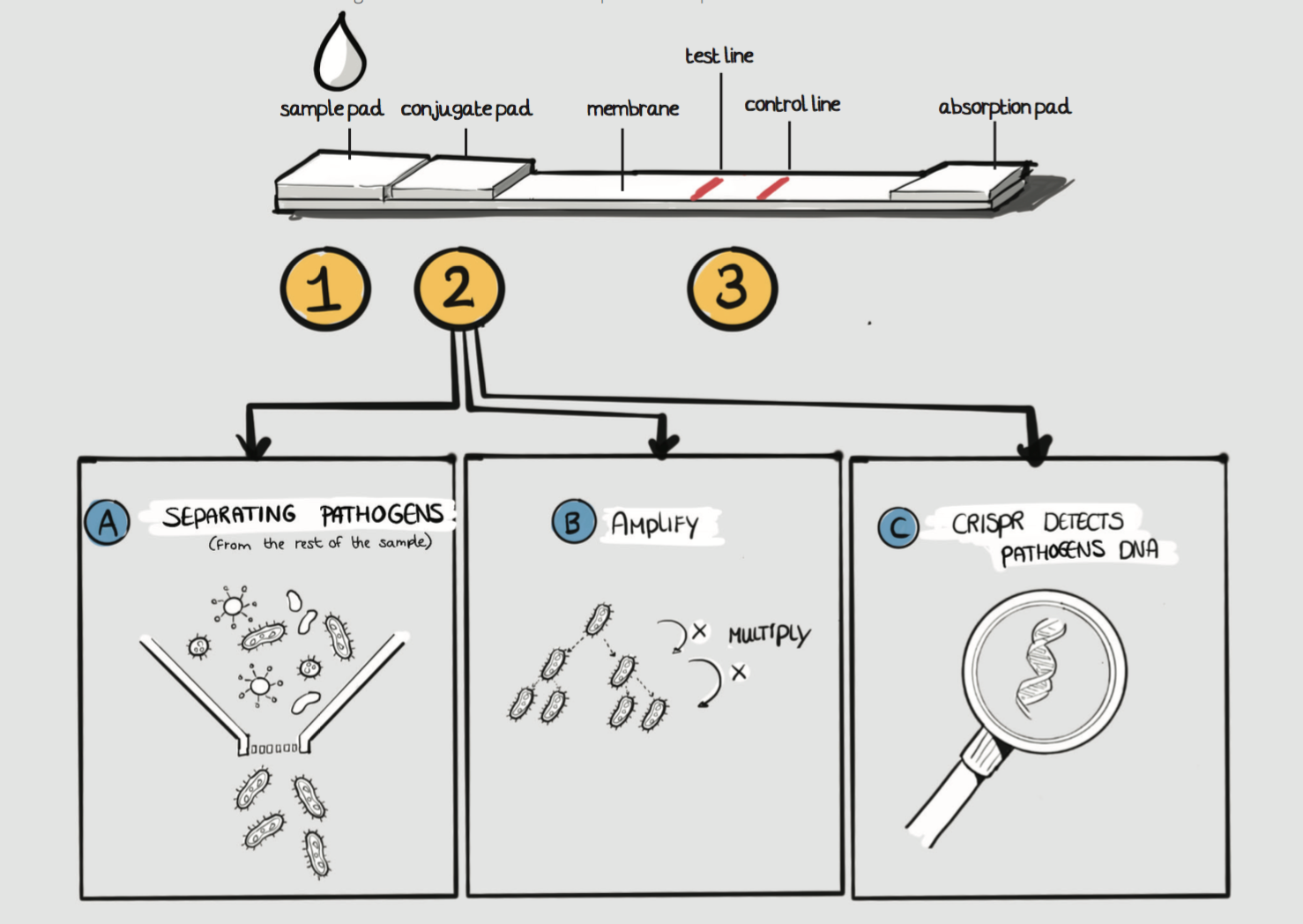
Thus, there is a need for a more reliable diagnostic test for the African VL context. The technical principle can be integrated on a diagnostic test strip to test a patient for VL. Based on a sample, it can separate and amplify the pathogens and detect their DNA with a CRISPR/Cas9 system. The result is a colourimetric read-out which indicates whether or not the patient has VL. This technical principle is based on DNA detection, which enables reliable test results independent of someone’s immune system. Additional advantages of this technical principle are that it is quick and broadly applicable.
Collaboration between IDE and Applied Science
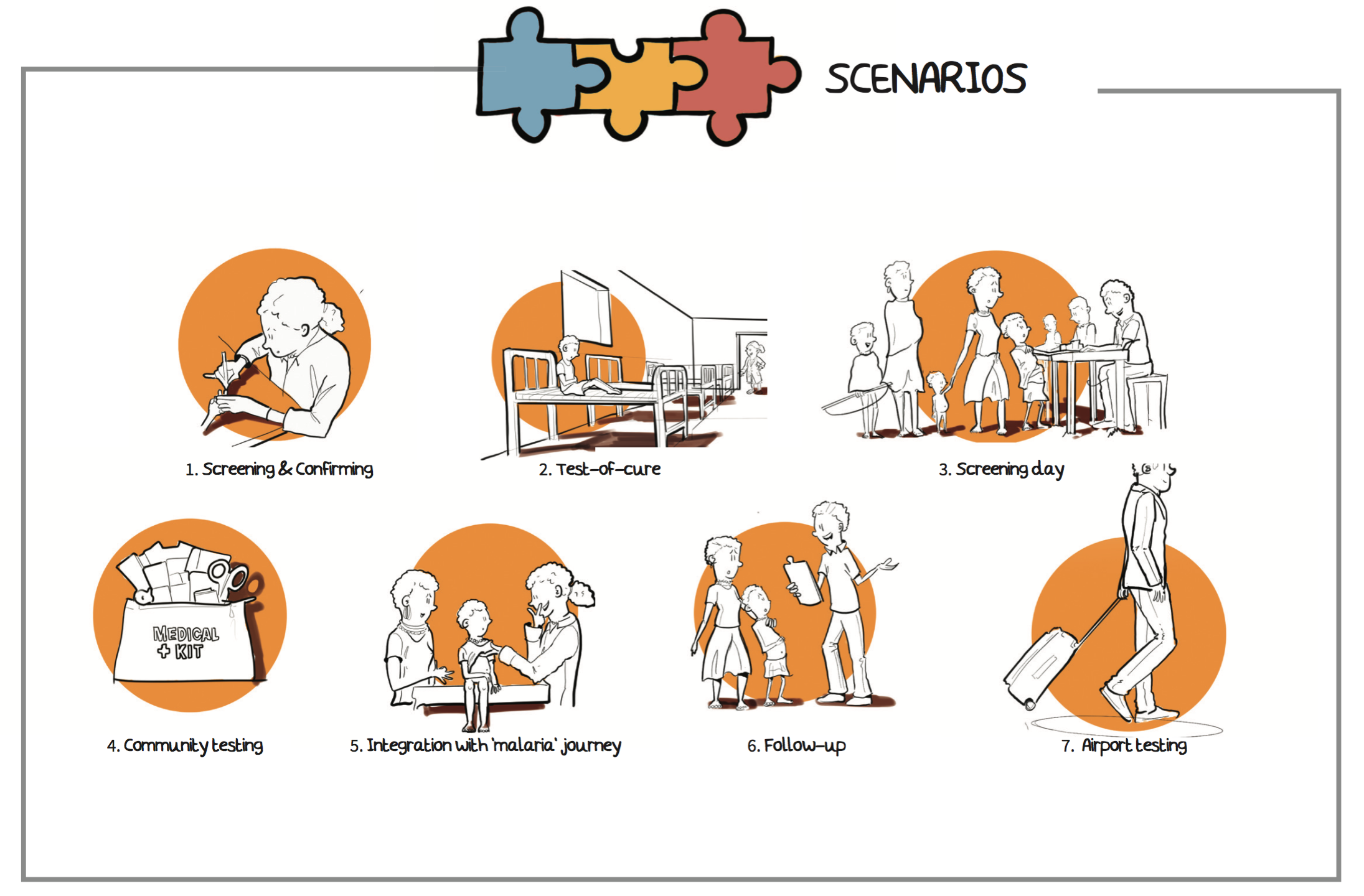
To understand where the technical principle could be implemented, a session was held with the team of IDE and Applied Sciences (TUDelft). This session resulted in the creation of seven scenarios which represent unique ways to combine the features of the technical principle into a diagnostic test which fits a diagnostic setting in the context of VL and matches a local need.
The most promising scenarios
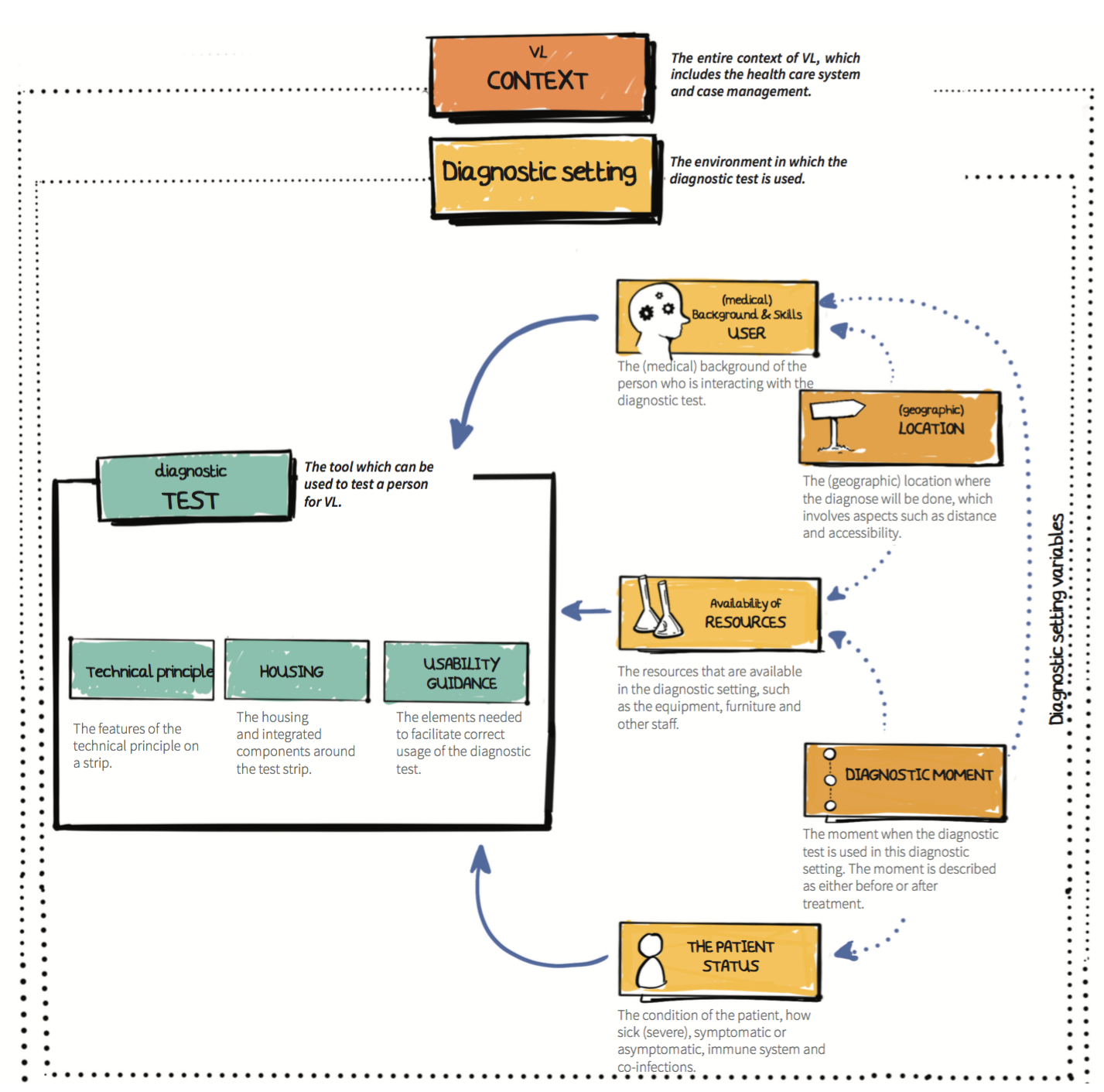
After evaluation with Médecins Sans Frontières, the two most ‘promising’ scenarios are selected based on the feasibility of the technical principle, the contextual fit and the local need. The two selected scenarios are: ‘Screening & Confirming” scenario and the “Test-of-cure” scenario.By detailing the selected scenarios, five variables where identified which clarify that the diagnostic setting influences the features of a diagnostic test. These are: 1) (geographic) location, 2) resource availability, 3) (medical) background of the user, 4) diagnostic moment, 5) patient status. Requirements are composed to see how the diagnostic setting affects the diagnostic test. The categorisation of the requirements and diagnostic setting variables have resulted in four different diagnostic tests - each with a unique set of requirements.
Contributions
A.P. ten Bosch (MSc thesis & Illustrations and pictures)
Dr. Ir. J.C. Diehl and Prof. Dr. J. M. L van Engelen
Industrial Design Engineering l Delft University of Technology
M.B. Bengtson (PhD candidate), Dr. M. Bharadwaj and Prof. Dr. C. Dekker
Department of Bionanoscience, Kavli Institute of Nanoscience,
Faculty of Applied Sciences l Delft University of Technology

Prof. Dr. Cees Dekker

Dr. Ir. Jan-Carel Diehl
- +31 (0)15 27 89729
- J.C.Diehl@tudelft.nl
-
Room B-3-350
Landbergstraat 15,
Delft University of Technology