Archive
27 August 2020
Researchers take important step towards new generation of batteries

Delft University of Technology researchers, in collaboration with researchers from Tsinghua University, have taken an important step towards a new type of Li-ion battery, which can be found in our smartphones, laptops and electric cars, among other things. For the first time, they succeeded in making an electrolyte that goes well with an anode made of lithium metal. Lithium metal is the holy grail for anodes. In theory, a two to three times higher energy density can be achieved with this material compared to current batteries.
27 August 2020
Two bits in one atom
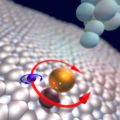
Researchers at Delft University of Technology have succeeded in independently manipulating two different types of magnetism within a single atom. The results are relevant for the development of extremely small forms of data storage. In time, this new discovery could make it possible to store two bits of information in one atom.
16 July 2020
Charting the way to minimal cells

Ironically, the closer we get to building a living cell, the less we are able to understand it. During the three-day virtual workshop “Reconstituting biology - charting the way to minimal cells”, cell-building researchers agreed this complexity is what makes cells so interesting.
16 July 2020
New: Online TU Delft summer course Pre-University Physics (start 3 August)

Never before have technology and innovation been so central to our society. Physics allows us to understand both simple everyday phenomena and the latest technologies: from guitar music to the 5G network. Physics is therefore indispensable for many educational programmes and other disciplines.
25 June 2020
Researchers create a mechanically-tunable graphene quantum dot

The ability to precisely manipulate individual charge carriers is a cornerstone for single-electron transistors and for electronic devices of the future, including solid-state quantum bits (qubits). Quantum dots (QDs) are at the heart of these devices. In a recent Nano Letters paper, researchers at Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) present the first mechanically-tunable monolayer graphene QD whose electronic properties can be modified by in-plane nanometer displacements.
25 June 2020
First detector array delivered to GUSTO mission

The first detector array for NASA's GUSTO mission has passed its pre-shipment review and is now shipping to the University of Arizona for integration into the balloon observatory. SRON together with TU Delft develops GUSTO's three 8-pixel-arrays, for the frequencies 4.7, 1.9 and 1.4 terahertz. They have now finished the array for the 4.7 terahertz channel—the most challenging part. GUSTO is a balloon mission that will measure emissions from cosmic material between stars.
19 June 2020
Spinoza Prize for Nynke Dekker

NWO has announced that TU Delft's Nynke Dekker has been awarded an NWO Spinoza Prize. The Spinoza and Stevin Prizes are the most prestigious awards in Dutch science. Besides Nynke Dekker, prizes were also awarded to prof. dr. ir. Jan van Hest (TUE), prof. dr. Pauline Kleingeld (RUG) and prof. dr. Sjaak Neefjes (LUMC/UL). Prof. dr. Linda Steg (RUG) en prof. dr. Ton Schumacher (AVL/LUMC/UL) have been awarded a Stevinprize. Each of the laureates will receive 2.5 million euros to spend on scientific research and related activities.
02 June 2020
TU Delft launches first eight TU Delft AI Labs

How can artificial intelligence (AI) accelerate scientific progress? Delft scientists will investigate this question in eight new 'TU Delft AI Labs'.
01 June 2020
Researchers develop method to probe phase transitions in 2D-materials
Phase transitions play an important role in materials. However, in two-dimensional materials, the most famous of which is graphene, phase transitions can be very difficult to study. Researchers from Delft University of Technology and the University of Valencia have developed a new method that helps to solve this problem. They suspended ultrathin layers of 2D-materials over a cavity and tracked the resonance frequency of the resulting membranes using lasers. The results of their work have been published in Nature Communications.
28 May 2020